Home > Press > Scientists see the light on microsupercapacitors: Rice University's laser-induced graphene makes simple, powerful energy storage possible
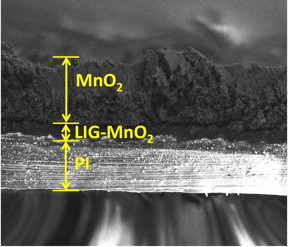 |
| Treating laser-induced graphene created at Rice University with manganese dioxide turns the material into a microsupercapacitor that rivals any on the market today, according to the researchers. The flexible material in this electron microscope image shows promise for electronics and apparel. Credit: Tour Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
ice University researchers who pioneered the development of laser-induced graphene have configured their discovery into flexible, solid-state microsupercapacitors that rival the best available for energy storage and delivery.
Scientists see the light on microsupercapacitors: Rice University's laser-induced graphene makes simple, powerful energy storage possible
Houston, TX | Posted on December 3rd, 2015The devices developed in the lab of Rice chemist James Tour are geared toward electronics and apparel. They are the subject of a new paper in the journal Advanced Materials.
Microsupercapacitors are not batteries, but inch closer to them as the technology improves. Traditional capacitors store energy and release it quickly (as in a camera flash), unlike common lithium-ion batteries that take a long time to charge and release their energy as needed.
Rice's microsupercapacitors charge 50 times faster than batteries, discharge more slowly than traditional capacitors and match commercial supercapacitors for both the amount of energy stored and power delivered.
The devices are manufactured by burning electrode patterns with a commercial laser into plastic sheets in room-temperature air, eliminating the complex fabrication conditions that have limited the widespread application of microsupercapacitors. The researchers see a path toward cost-effective, roll-to-roll manufacturing.
"It's a pain in the neck to build microsupercapacitors now," Tour said. "They require a lot of lithographic steps. But these we can make in minutes: We burn the patterns, add electrolyte and cover them."
Their capacitance of 934 microfarads per square centimeter and energy density of 3.2 milliwatts per cubic centimeter rival commercial lithium thin-film batteries, with a power density two orders of magnitude higher than batteries, the researchers claimed. The devices displayed long life and mechanical stability when repeatedly bent 10,000 times.
Their energy density is due to the nature of laser-induced graphene (LIG). Tour and his group discovered last year that heating a commercial polyimide plastic sheet with a laser burned everything but the carbon from the top layer, leaving a form of graphene. But rather than a flat sheet of hexagonal rings of atoms, the laser left a spongy array of graphene flakes attached to the polyimide, with high surface area.
The researchers treated their LIG patterns -- interdigitated like folded hands -- with manganese dioxide, ferric oxyhydroxide or polyaniline through electrodeposition and turned the resulting composites into positive and negative electrodes. The composites could then be formed into solid-state microsupercapacitors with no need for current collectors, binders or separators.
Tour is convinced the day is coming when supercapacitors replace batteries entirely, as energy storage systems will charge in minutes rather than hours. "We're not quite there yet, but we're getting closer all the time," he said. "In the interim, they're able to supplement batteries with high power. What we have now is as good as some commercial supercapacitors. And they're just plastic."
Rice graduate students Lei Li and Jibo Zhang and alumnus Zhiwei Peng are lead authors of the paper. Co-authors are Rice postdoctoral researchers Yongsung Ji, Nam Dong Kim, Gedeng Ruan and Yang Yang and graduate students Yilun Li, Ruquan Ye and Huilong Fei; Caitian Gao, a visiting graduate student at Rice from Lanzhou University, China; and Qifeng Zhong, a visiting graduate student at Rice from Southeast University, Nanjing, China.
Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of materials science and nanoengineering and of computer science.
The Air Force Office of Scientific Research and its Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative and the Chinese Scholarship Council supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,888 undergraduates and 2,610 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Textiles/Clothing
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
![]() Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








