Home > Press > Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process
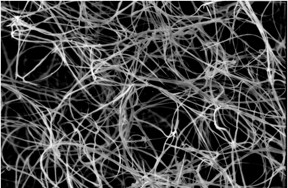 |
| A tangle of unprocessed boron nitride nanotubes seen through a scanning electron microscope. Rice University scientists introduced a method to combine them into fibers using the custom wet-spinning process they developed to make carbon nanotube fibers. (Credit: Pasquali Research Group/Rice University) |
Abstract:
Boron nitride nanotubes used to be hard to process, according to Rice University researchers. Not anymore.
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process
Houston, TX | Posted on June 24th, 2022A Rice team led by professors Matteo Pasquali and Angel Martí has simplified handling of the highly valuable nanotubes to make them more suitable for large-scale applications, including aerospace, electronics and energy-efficient materials.
The researchers reported in Nature Communications that boron nitride nanotubes, aka BNNTs, assemble themselves into liquid crystals under the right conditions, primarily concentrations above 170 parts per million by weight in chlorosulfonic acid.
These liquid crystals consist of aligned BNNTs that are far easier to process than the tangled nanotubes that usually form in solution. The lab proceeded to form fibers and films from the liquid crystalline solutions.
“BNNT fibers are attractive for the manufacture of a variety of products, with applications that range from wearables to aerospace vehicles,” said Martí, whose lab designed solutions and helped characterize the fibers produced in Pasquali’s lab.
Boron nitride nanotubes are like carbon nanotubes, but with alternating boron and nitrogen atoms instead of carbon in their hexagonal lattices. Both types of nanotubes are strong, but unlike electrically conductive carbon nanotubes, BNNTs are good electrical insulators and are thermally and chemically stable in air up to 900 degrees Celsius (1,652 degrees Fahrenheit).
To form liquid crystals, the researchers needed to be sure their nanotubes were free of contaminants. Unfortunately, those contaminants were mostly bits of boron nitride that threatened to gum up the works.
“Early BNNT samples contained lots of non-nanotube boron nitride structures,” said graduate student and lead author Cedric Ginestra. “They were either chemically bound to the BNNTs or just physically adhered in a way that prevented BNNTs from dispersing in acid and aligning at higher concentrations.
“It is difficult to separate these boron nitride allotropes from BNNTs, and hard to even measure their concentration,” he said. “All the different types of boron nitride appear identical by basically every quantitative technique that we’ve tried so far.”
Working with their supplier to optimize their BNNT purification process for the formation of liquid crystalline solutions and using a purification process developed in the Pasquali lab helped them obtain better batches of BNNTs, he said. Once suitable material was produced, the Pasquali group was primed to quickly adapt its wet-spinning techniques for carbon nanotube fibers to make the first boron nitride threads with the process.
“There are reports of others taking solid puffs of BNNTs and stretching and twisting them to make a yarn, but that’s very different from our process,” Ginestra said. “Our goal was to make a very highly aligned fiber because the properties are better along the length of the nanotubes.”
Liquid crystals are the ideal precursor for fibers because the nanotubes within are already aligned, he said. BNNT alignment in the liquid crystals was identified microscopically by their birefringence, a phenomenon by which crystals split light, prism-like, even if they appear to be clear.
The films also demonstrated how BNNT solution processing can adopt methods developed for carbon nanotubes, Ginestra said. Such transparent thin films could be useful in next-generation electronics. “The BNNT film and fiber properties will improve as the material and our understanding of the liquid crystalline solution improves,” he said.
Martí noted BNNT films would be useful as filters for ultraviolet light, antifouling coatings and for corrosion protection.
Co-authors of the paper are Rice graduate students Cecilia Martínez-Jiménez and Oliver Dewey, alumni Ashleigh Smith McWilliams, Robert Headrick and Dmitry Kosynkin and postdoctoral researcher Jesus Acapulco; graduate student Asia Matatyaho Ya’akobi and professor emeritus Yeshayahu Talmon of the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology and the Russell Berrie Nanotechnology Institute, Haifa, Israel; Lyndsey Scammell and Michael Smith of BNNT LLC, Newport News, Virginia; former Rice postdoctoral researcher Daniel Marincel, now an assistant professor at the Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology, Terre Haute, Indiana; senior researcher Cheol Park of the NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia; and associated research fellow Sang-Hyon Chu of the National Institute of Aerospace, Hampton, Virginia.
Martí is a professor of chemistry, bioengineering and materials science and nanoengineering. Pasquali is the A.J. Hartsook Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, a professor of chemistry and of materials science and nanoengineering and director of the Carbon Hub.
The research was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (FA9550-18-1-0014, FA9550-19-1-7045), the Welch Foundation (C-1668), the National Council of Science and Technology (CONACyT) Mexico (710115), a NASA Space Technology Research Fellowship (NNX14AL71H), the National Science Foundation (1807737, 2108838), the Department of Energy (DE-AR0001015), the United States-Israel Binational Science Foundation (2016161) and an Office of Naval Research Small Business Innovation Research grant (N68335-19-C-0560).
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 4,240 undergraduates and 3,972 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 1 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Aerospace/Space
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
![]() The National Space Society Congratulates SpaceX on Starship’s 7th Test Flight: Latest Test of the Megarocket Hoped to Demonstrate a Number of New Technologies and Systems January 17th, 2025
The National Space Society Congratulates SpaceX on Starship’s 7th Test Flight: Latest Test of the Megarocket Hoped to Demonstrate a Number of New Technologies and Systems January 17th, 2025
Industrial
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








