Home > Press > New class of 3D-printed aerogels improve energy storage
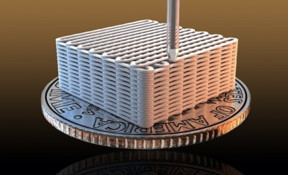 |
| Lawrence Livermore researchers have made graphene aerogel microlattices with an engineered architecture via a 3D printing technique known as direct ink writing. Photo by Ryan Chen/LLNL |
Abstract:
A new type of graphene aerogel will make for better energy storage, sensors, nanoelectronics, catalysis and separations.
New class of 3D-printed aerogels improve energy storage
Livermore, CA | Posted on April 22nd, 2015Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers have made graphene aerogel microlattices with an engineered architecture via a 3D printing technique known as direct ink writing. The research appears in the April 22 edition of the journal, Nature Communications.
The 3D printed graphene aerogels have high surface area, excellent electrical conductivity, are lightweight, have mechanical stiffness and exhibit supercompressibility (up to 90 percent compressive strain). In addition, the 3D printed graphene aerogel microlattices show an order of magnitude improvement over bulk graphene materials and much better mass transport.
Aerogel is a synthetic porous, ultralight material derived from a gel, in which the liquid component of the gel has been replaced with a gas. It is often referred to as "liquid smoke."
Previous attempts at creating bulk graphene aerogels produce a largely random pore structure, excluding the ability to tailor transport and other mechanical properties of the material for specific applications such as separations, flow batteries and pressure sensors.
"Making graphene aerogels with tailored macro-architectures for specific applications with a controllable and scalable assembly method remains a significant challenge that we were able to tackle," said engineer Marcus Worsley, a co-author of the paper. "3D printing allows one to intelligently design the pore structure of the aerogel, permitting control over mass transport (aerogels typically require high pressure gradients to drive mass transport through them due to small, tortuous pore structure) and optimization of physical properties, such as stiffness. This development should open up the design space for using aerogels in novel and creative applications."
During the process, the graphene oxide (GO) inks are prepared by combining an aqueous GO suspension and silica filler to form a homogenous, highly viscous ink. These GO inks are then loaded into a syringe barrel and extruded through a micronozzle to pattern 3D structures.
"Adapting the 3D printing technique to aerogels makes it possible to fabricate countless complex aerogel architectures for a broad range of applications including its mechanical properties and compressibility, which has never been achieved before, " said engineer Cheng Zhu, the other co-author of the journal article.
###
Other Livermore researchers include Yong-Jin Han, Eric Duoss, Alexandra Golobic, Joshua Kuntz and Christopher Spadaccini. The work is funded by the Laboratory Directed Research and Development Program.
####
About DOE/Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Founded in 1952, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory provides solutions to our nation's most important national security challenges through innovative science, engineering and technology. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is managed by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anne Stark
925-422-9799
Copyright © DOE/Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Nature Communications "Highly compressible 3D periodic graphene aerogel microlattices":
Nature Communications "Highly compressible 3D periodic graphene aerogel microlattices":
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
3D & 4D printing/Additive-manufacturing
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
![]() 3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
Aerogels
![]() The lightest shielding material in the world: Protection against electromagnetic interference July 3rd, 2020
The lightest shielding material in the world: Protection against electromagnetic interference July 3rd, 2020
![]() Super-light, super-insulating ceramic aerogel keeps the hottest temperatures at bay February 17th, 2019
Super-light, super-insulating ceramic aerogel keeps the hottest temperatures at bay February 17th, 2019
![]() Researchers reduce expensive noble metals for fuel cell reactions August 22nd, 2016
Researchers reduce expensive noble metals for fuel cell reactions August 22nd, 2016
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








