Home > Press > Nano-engineering electrodes to give tiny generators a boost
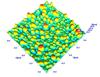 |
| A 3D atomic force microscope topography image of metallic nanoparticles deposited on graphite. |
Abstract:
Could our waste be part of the answer to humanity's energy problems? Some researchers think so, thanks to bacteria that chow down on everything from sewage to heavy metals and give off electricity as one of their own waste products.
Nano-engineering electrodes to give tiny generators a boost
Okinawa, Japan | Posted on September 21st, 2012But as with many great ideas, the devil is in the details. OIST's Biological Systems Unit is one of the research groups now working on making waste-fueled microbial fuel cells (MFCs) cheap and efficient enough for real-world applications.
One great challenge in achieving that goal is designing sturdy, cheap electrodes for MFCs that conduct electricity well, resist corrosion, and won't poison bacteria that cling to their surfaces. To this end, the Nanoparticles by Design Unit is working with the Biological Systems Unit to build and test new types of nanoparticle-studded electrodes. The idea is to coat a core of cheap material with a very thin layer of a more expensive, biocompatible metal, then stick the resulting nanoparticles onto the surface of a carbon electrode. In addition to harnessing the properties of the expensive metal at minimal cost, this will increase the surface area of the electrode so that it can host more electricity-generating bacteria.
Other researchers have found that nanoparticle-studded carbon electrodes increase the electricity output of MFCs up to 20-fold compared with plain carbon electrodes; Nanoparticles by Design Unit head Mukhles Sowwan hopes to increase this by experimenting with different sizes, compositions, and methods of pinning the nanoparticles to the electrode surface. Says Sowwan, "I believe that this innovative multidisciplinary approach in applying cutting-edge research could lead to the development of efficient microbial fuel cells."
####
About Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology - OIST
The Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology is an interdisciplinary graduate school offering a 5-year PhD program in Science. Over half of the faculty and students are recruited from outside Japan, and all education and research is conducted entirely in English. OIST researchers are conducting multi-disciplinary research in five major areas: Neuroscience, Molecular Sciences, Environmental and Ecological Sciences, Physical Sciences, and Mathematical Computational Sciences. In the six years leading up to graduate school accreditation, OIST received recognition for doing original research and sponsoring innovative international workshops and courses.
The graduate school accepts 20 students per year, creating a very low student to instructor ratio. Students also receive support for living costs, health care, housing, childcare, and other needs that would otherwise distract them from the science. Balancing lectures and lab work, the doctoral program places students in well-funded labs where they work side-by-side with top researchers on state-of-the-art equipment. Frequent visits from internationally-known scientists further enrich the program and provide opportunities for collaboration and exchange. By the time they graduate, students have accumulated not only abstract knowledge and practical skills but also the kind of professional connections necessary to launch their careers as world-class researchers.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Neil Calder
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








