Home > Press > Lattice-driven charge density wave fluctuations far above the transition temperature in Kagome superconductor
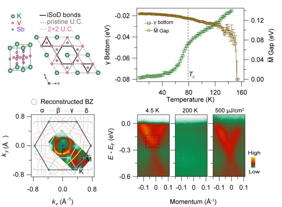 |
| The CDW-related band folding and the band gap persist up to 150 K, indicates strong fluctuating CDW far above its CDW transition temperature (78 K). Credit ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
The study of charge density wave (CDW) phenomena in superconductors has long been central to understanding the complex interactions governing quantum materials. In particular, the relationship between CDWs and superconductivity has been intensely debated. Recent findings on kagome superconductors have opened up new possibilities by observing unusual CDW behavior in the KV₃Sb₅ compound, a material that has gained attention for its unique kagome lattice structure and electronic correlations. Despite the long-held view that CDWs emerge below certain critical temperatures, researchers have now shown that KV₃Sb₅ exhibits significant lattice-driven CDW fluctuations at temperatures far exceeding its CDW transition, providing novel insights into the underlying mechanisms.
Lattice-driven charge density wave fluctuations far above the transition temperature in Kagome superconductor
Beijing, China | Posted on April 25th, 2025In a recent study published in Science Bulletin, researchers from the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and ShanghaiTech University explored the nature of these lattice-driven CDW fluctuations in KV₃Sb₅. Their work, titled “Fluctuated Lattice-Driven Charge Density Wave Far Above the Condensation Temperature in Kagome Superconductor KV₃Sb₅,” investigates how the CDW state evolves with temperature and laser pump, and how these fluctuations influence the material’s electronic structure.
To study this phenomenon, the research team synthesized high-quality single crystals of KV₃Sb₅ and used time- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (TRARPES) to observe the evolution of its electronic structure at varying temperatures and pump fluence. Their findings reveal that in-plane CDW-related band folding and lattice distortions are present at temperatures up to 150 K, which is significantly higher than the CDW transition temperature of 78 K. By conducting ultrafast pump-probe experiments, the team discovered that when the pump fluence surpasses a critical threshold, out-of-plane CDW order can be transiently suppressed via rapid screening of electron correlations. A comparison of the energy shifts of characteristic bands under thermal excitation and ultrafast optical pump shows remarkably similar magnitudes. This observation underscores that the full three-dimensional (3D) CDW condensation primarily hinges on electronic correlations. These findings provide critical insights into the complex interactions between the electrons and the lattice in KV₃Sb₅, deepening our understanding of how CDWs form and evolve in this novel material.
By delivering new insights into the roles of the lattice and electronic correlations in determining 3D CDW behavior, this study paves the way for further exploration of kagome superconductors. Future research will concentrate on higher energy-resolution measurements and the influence of multi-dimensional field tuning to deepen our understanding of complex quantum phase competition in these intriguing materials.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Bei Yan
Science China Press
Expert Contact
Weotao Zhang
Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








