Home > Press > Controlling the speed of enzyme motors brings biomedical applications of nanorobots closer: Recent advances in this field have made micro- and nanomotors promising devices for solving many biomedical problems
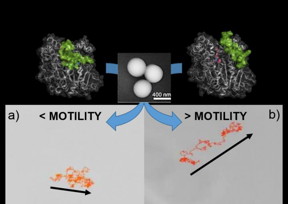 |
| a) Trajectory of an enzyme-powered nanomotor prepared with lipase in a closed conformation and without controlled orientation during immobilization on the silicon nanoparticle surface. b) Trajectory of an enzyme-powered nanomotor prepared with lipase in an open conformation and with controlled orientation during immobilization on the silicon nanoparticle Surface. The central panel shows a scanning electron microscopy image of nanomotors like those used in the experiment. CREDIT CNIC/ IBEC |
Abstract:
A study by scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC), the Universidad Complutense (UCM), Universidad de Girona (UdG), and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), working together with other international centers, has overcome one of the key hurdles to the use of nanorobots powered by lipases, enzymes that play essential roles in digestion by breaking down fats in foods so that they can be absorbed.
Controlling the speed of enzyme motors brings biomedical applications of nanorobots closer: Recent advances in this field have made micro- and nanomotors promising devices for solving many biomedical problems
Madrid, Spain | Posted on October 13th, 2020The study was coordinated by Marco Filice of the CNIC Microscopy and Dynamic Imaging Unit--part of the ReDIB Infraestructura Científico Técnica Singular (ICTS)--, professor at Pharmacy Faculty (UCM) and ICREA Research Professor Samuel Sánchez of the IBEC. The article, published in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition, describes a tool for modulating motors powered by enzymes, broadening their potential biomedical and environmental applications.
Microorganisms are able to swim through complex environments, respond to their surroundings, and organize themselves autonomously. Inspired by these abilities, over the past 20 years scientists have managed to artificially replicate these tiny swimmers, first at the macro-micro scale and then at the nano scale, finding applications in environmental remediation and biomedicine.
"The speed, load-bearing capacity, and ease of surface functionalization of micro and nanomotors has seen recent research advances convert these devices into promising instruments for solving many biomedical problems. However, a key challenge to the wider use of these nanorobots is choosing an appropriate motor to propel them," explained Sánchez.
Over the past 5 years, the IBEC group has pioneered the use of enzymes to generate the propulsive force for nanomotors. "Bio-catalytic nanomotors use biological enzymes to convert chemical energy into mechanical force, and this approach has sparked great interest in the field, with urease, catalase, and glucose oxidase among the most frequent choices to power these tiny engines," said Sánchez.
The CNIC group is a leader in the structural manipulation and immobilization of lipase enzymes on the surface of different nanomaterials. Lipases make excellent nanomotor components because their catalytic mechanism involves major conformational changes between an open, active form and a closed,
"In this project, we investigated the effect of modulating the catalytic activity of lipase enzymes to propel silicon-based nanoparticles," explained Filice.
In addition to the 3-dimensional conformation of the enzyme, the team also investigated how controlling the orientation of the enzyme during its immobilization on the nanomotor surface affects its catalytic activity and therefore the propulsion of the nanorobots.
The researchers chemically modified the surface of silicon nanoparticles to generate three specific combinations of lipase conformations and orientations during immobilization: 1) open conformation plus controlled orientation; 2) closed conformation plus uncontrolled orientation; 3) a situation intermediate between 1 and 2.
The team analyzed the three types of nanorobot with spectroscopic techniques, assays to assess catalytic parameters related to enzyme activity, Dynamic Molecular simulations (performed by Professor Silvia Osuna's team at UdG), and direct tracking of individual nanomotor trajectories by microscopy techniques. "The results demonstrate that combining an open enzyme conformation with a specific orientation on the nanomotor is critical to achieving controlled propulsion."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Fátima Lois
34-639-282-477
@CNIC_CARDIO
Copyright © Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Robotics
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
![]() Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
![]() Kavli Lectures: The art of building small and innovating for industrial impact August 7th, 2020
Kavli Lectures: The art of building small and innovating for industrial impact August 7th, 2020
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








