Home > Press > New type of solar structure cools buildings in full sunlight
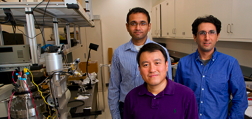 |
| Professor Shanhui Fan (center) with graduate students Aaswath Raman (left) and Eden Rephaeli (right). Photo: Norbert von der Groeben |
Abstract:
A Stanford team has designed an entirely new form of cooling panel that works even when the sun is shining. Such a panel could vastly improve the daylight cooling of buildings, cars and other structures by radiating sunlight back into the chilly vacuum of space.
New type of solar structure cools buildings in full sunlight
Stanford, CA | Posted on March 27th, 2013Homes and buildings chilled without air conditioners. Car interiors that don't heat up in the summer sun. Tapping the frigid expanses of outer space to cool the planet. Science fiction, you say? Well, maybe not any more.
A team of researchers at Stanford has designed an entirely new form of cooling structure that cools even when the sun is shining. Such a structure could vastly improve the daylight cooling of buildings, cars and other structures by reflecting sunlight back into the chilly vacuum of space. Their paper describing the device was published March 5 in Nano Letters.
"People usually see space as a source of heat from the sun, but away from the sun outer space is really a cold, cold place," explained Shanhui Fan, professor of electrical engineering and the paper's senior author. "We've developed a new type of structure that reflects the vast majority of sunlight, while at the same time it sends heat into that coldness, which cools manmade structures even in the day time."
The trick, from an engineering standpoint, is two-fold. First, the reflector has to reflect as much of the sunlight as possible. Poor reflectors absorb too much sunlight, heating up in the process and defeating the purpose of cooling.
The second challenge is that the structure must efficiently radiate heat back into space. Thus, the structure must emit thermal radiation very efficiently within a specific wavelength range in which the atmosphere is nearly transparent. Outside this range, Earth's atmosphere simply reflects the light back down. Most people are familiar with this phenomenon. It's better known as the greenhouse effect—the cause of global climate change.
Two goals in one
The new structure accomplishes both goals. It is an effective a broadband mirror for solar light—it reflects most of the sunlight. It also emits thermal radiation very efficiently within the crucial wavelength range needed to escape Earth's atmosphere.
Radiative cooling at nighttime has been studied extensively as a mitigation strategy for climate change, yet peak demand for cooling occurs in the daytime.
"No one had yet been able to surmount the challenges of daytime radiative cooling—of cooling when the sun is shining," said Eden Rephaeli, a doctoral candidate in Fan's lab and a co-first-author of the paper. "It's a big hurdle."
The Stanford team has succeeded where others have come up short by turning to nanostructured photonic materials. These materials can be engineered to enhance or suppress light reflection in certain wavelengths.
"We've taken a very different approach compared to previous efforts in this field," said Aaswath Raman, a doctoral candidate in Fan's lab and a co-first-author of the paper. "We combine the thermal emitter and solar reflector into one device, making it both higher performance and much more robust and practically relevant. In particular, we're very excited because this design makes viable both industrial-scale and off-grid applications."
Using engineered nanophotonic materials the team was able to strongly suppress how much heat-inducing sunlight the panel absorbs, while it radiates heat very efficiently in the key frequency range necessary to escape Earth's atmosphere. The material is made of quartz and silicon carbide, both very weak absorbers of sunlight.
Net cooling power
The new device is capable of achieving a net cooling power in excess of 100 watts per square meter. By comparison, today's standard 10-percent-efficient solar panels generate the about the same amount of power. That means Fan's radiative cooling panels could theoretically be substituted on rooftops where existing solar panels feed electricity to air conditioning systems needed to cool the building.
To put it a different way, a typical one-story, single-family house with just 10 percent of its roof covered by radiative cooling panels could offset 35 percent its entire air conditioning needs during the hottest hours of the summer.
Radiative cooling has another profound advantage over all other cooling strategy such as air-conditioner. It is a passive technology. It requires no energy. It has no moving parts. It is easy to maintain. You put it on the roof or the sides of buildings and it starts working immediately.
A changing vision of cooling
Beyond the commercial implications, Fan and his collaborators foresee a broad potential social impact. Much of the human population on Earth lives in sun-drenched regions huddled around the equator. Electrical demand to drive air conditioners is skyrocketing in these places, presenting an economic and an environmental challenge. These areas tend to be poor and the power necessary to drive cooling usually means fossil-fuel power plants that compound the greenhouse gas problem.
"In addition to these regions, we can foresee applications for radiative cooling in off-the-grid areas of the developing world where air conditioning is not even possible at this time. There are large numbers of people who could benefit from such systems," Fan said.
Andrew Myers is associate director of communications for the Stanford University School of Engineering.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andrew Myers
650-736-2245
Copyright © Stanford School of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Home
![]() Nanomaterials enable dual-mode heating and cooling device: Device could cut HVAC energy use by nearly 20% in the US December 2nd, 2020
Nanomaterials enable dual-mode heating and cooling device: Device could cut HVAC energy use by nearly 20% in the US December 2nd, 2020
![]() Bosch Sensortec launches ideation community to foster and accelerate innovative IoT applications : Creativity hub for customers, partners, developers and makers February 18th, 2019
Bosch Sensortec launches ideation community to foster and accelerate innovative IoT applications : Creativity hub for customers, partners, developers and makers February 18th, 2019
![]() Iran Develops Water-Repellent Nano-Paint December 5th, 2018
Iran Develops Water-Repellent Nano-Paint December 5th, 2018
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Construction
![]() Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








