Home > Press > Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy
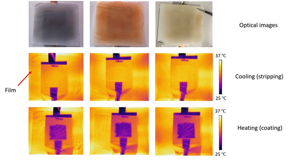 |
| The material contains a layer that can take on two conformations: solid copper that retains most infrared heat, which helps keep the building warm; or a watery solution that emits infrared, which can help cool the building. CREDIT University of Chicago PME - Image courtesy of Hsu Group |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) have designed a chameleon-like building material that changes its infrared color—and how much heat it absorbs or emits—based on the outside temperature. On hot days, the material can emit up to 92 percent of the infrared heat it contains, helping cool the inside of a building. On colder days, however, the material emits just 7 percent of its infrared, helping keep a building warm.
Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy
Chicago, IL | Posted on January 27th, 2023“We’ve essentially figured out a low-energy way to treat a building like a person; you add a layer when you’re cold and take off a layer when you’re hot,” said Asst. Prof. Po-Chun Hsu, who led the research published in Nature Sustainability. “This kind of smart material lets us maintain the temperature in a building without huge amounts of energy.”
Driven by climate change
According to some estimates, buildings account for 30 percent of global energy consumption and emit 10 percent of all global greenhouse gas. About half of this energy footprint is attributed to the heating and cooling of interior spaces.
“For a long time, most of us have taken our indoor temperature control for granted, without thinking about how much energy it requires,” said Hsu. “If we want a carbon-negative future, I think we have to consider diverse ways to control building temperature in a more energy-efficient way.”
Researchers have previously developed radiative cooling materials that help keep buildings cool by boosting their ability to emit infrared, the invisible heat that radiates from people and objects. Materials also exist that prevent the emission of infrared in cold climates.
“A simple way to think about it is that if you have a completely black building facing the sun, it’s going to heat up more easily than other buildings,” said PME graduate student Chenxi Sui, the first author of the new manuscript.
That kind of passive heating might be a good thing in the winter, but not in the summer.
As global warming causes increasingly frequent extreme weather events and variable weather, there is a need for buildings to be able to adapt; few climates require year-round heating or year-round air conditioning.
From metal to liquid and back
Hsu and colleagues designed a non-flammable “electrochromic” building material that contains a layer that can take on two conformations: solid copper that retains most infrared heat, or a watery solution that emits infrared. At any chosen trigger temperature, the device can use a tiny amount of electricity to induce the chemical shift between the states by either depositing copper into a thin film, or stripping that copper off.
In the new paper, the researchers detailed how the device can switch rapidly and reversibly between the metal and liquid states. They showed that the ability to switch between the two conformations remained efficient even after 1,800 cycles.
Then, the team created models of how their material could cut energy costs in typical buildings in 15 different U.S. cities. In an average commercial building, they reported, the electricity used to induce electrochromic changes in the material would be less than 0.2% of the total electricity usage of the building, but could save 8.4% of the building’s annual HVAC energy consumption.
“Once you switch between states, you don’t need to apply any more energy to stay in either state,” said Hsu. “So for buildings where you don’t need to switch between these states very frequently, it’s really using a very negligible amount of electricity.”
Scaling up
So far, Hsu’s group has only created pieces of the material that measure about six centimeters across. However, they imagine that many such patches of the material could be assembled like shingles into larger sheets. They say the material could also be tweaked to use different, custom colors—the watery phase is transparent and nearly any color can be put behind it without impacting its ability to absorb infrared.
The researchers are now investigating different ways of fabricating the material. They also plan to probe how intermediate states of the material could be useful.
“We demonstrated that radiative control can play a role in controlling a wide range of building temperatures throughout different seasons,” said Hsu. “We’re continuing to work with engineers and the building sector to look into how this can contribute to a more sustainable future.”
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Meredith Davis
University of Chicago
Copyright © University of Chicago
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Construction
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
![]() You're so vein: Scientists discover faster way to manufacture vascular materials May 14th, 2021
You're so vein: Scientists discover faster way to manufacture vascular materials May 14th, 2021
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








