Home > Press > Quantum chains in graphene nanoribbons: Breakthrough in nanoresearch
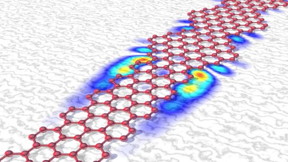 |
| When graphene nanoribbons contain sections of varying width, very robust new quantum states can be created in the transition zone. CREDIT Empa |
Abstract:
A material that consists of atoms of a single element, but has completely different properties depend-ing on the atomic arrangement - this may sound strange, but is actually reality with graphene nano-ribbons. The ribbons, which are only a few carbon atoms wide and exactly one atom thick, have very different electronic properties depending on their shape and width: conductor, semiconductor or insu-lator. An international research team led by Empa's
Quantum chains in graphene nanoribbons: Breakthrough in nanoresearch
St. Gallen, Switzerland | Posted on August 9th, 2018laboratory has now suc-ceeded in precisely adjusting the properties of the ribbons by specifically varying their shape. The par-ticular feature of this technology is that not only can the «usual» electronic properties mentioned above be varied - it can also be used to generate specific local quantum states.
So what's behind it? If the width of a narrow graphene nanoribbon changes, in this case from seven to nine atoms, a special zone is created at the transition: because the electronic properties of the two ar-eas differ in a special, so-called topological way, a «protected» and thus very robust new quantum state is created in the transition zone. This local electronic quantum state can now be used as a basic component to produce tailor-made semiconductors, metals or insulators - and possibly even as a component in quantum computers.
The Empa researchers under the lead of Oliver Gröning were able to show that if these ribbons are built with regularly alternating zones of different widths, a chain of interlinked quantum states with its own electronic structure is created by the numerous transitions. The exciting thing is that the electronic properties of the chain change depending on the width of the different segments. This allows them to be finely adjusted - from conductors to semiconductors with different bandgaps. This principle can be applied to many different types of transition zones - for example, from seven to eleven atoms.
«The importance of this development is also underlined by the fact that a research group at the Uni-versity of California, Berkeley, came to similar results independently of us,» said Gröning. The work of the US research team has been published in the same issue of Nature.
On the way to nanoelectronics
Based on these novel quantum chains, precise nano-transistors could be manufactured in the future - a fundamental step on the way to nanoelectronics. Whether the switching distance between the «1» state and the «0» state of the nanotransistor is actually large enough depends on the bandgap of the semiconductor - and with the new method this can be set almost at will.
In reality, however, this is not quite as simple: for the chain to have the desired electronic properties, each of the several hundred or even thousands of atoms must be in the right place. «This is based on complex, interdisciplinary research, » says Empa researcher Gröning. «Researchers from different disci-plines in Dübendorf, Mainz, Dresden, and Troy (USA) worked together - from theoretical understanding and specific knowledge of how precursor molecules have to be built and how structures on surfaces can be selectively grown to structural and electronic analysis using a scanning tunneling microscope.»
An excursion into the quantum realm
Ultrasmall transistors - and thus the next step in the further miniaturization of electronic circuits - are the obvious application possibilities here: although they are technically challenging, electronics based on nano-transistors actually work fundamentally the same as today's microelectronics. The semicon-ducting nanoribbons produced by the Empa researchers would allow transistors with a channel cross-section 1,000 times smaller than typically manufactured today. However, further possibilities can also be imagined, for example in the field of spintronics or even quantum informatics.
This is because the electronic quantum states at junctions of graphene nanoribbons of different widths can also carry a magnetic moment. This could make it possible to process information not by charge as was previously customary, but by the so-called spin - in the figurative sense the «direction of rota-tion» of the state. And the development could even go one step further. «We have observed that topological end states occur at the ends of certain quantum chains. This offers the possibility of using them as elements of so-called qubits - the complex, interlocked states in a quantum computer,» ex-plains Oliver Gröning.
Today and tomorrow, however, no quantum computer is built from nanoribbons - there is still a lot of research needed, says Gröning: «The possibility of flexibly adjusting the electronic properties through the targeted combination of individual quantum states represents a major leap for us in the production of new materials for ultra-miniaturized transistors.» The fact that these materials are stable under environmental conditions plays an important role in the development of future applications. "The further-reaching potential of the chains to create local quantum states and link them together in a targeted manner is also fascinating," Gröning continues. «Whether this potential can actually be ex-ploited for future quantum computers remains to be seen, however. It is not enough to create localized topological states in the nanoribbons - these would also have to be coupled with other materials such as superconductors in such a way that the conditions for qubits are actually met.»
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Oliver Gröning
41-587-654-669
Copyright © EMPA
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








