Home > Press > ‘Brand new physics’ for next generation spintronics: Physicists discover a unique quantum behavior that offers a new way to manipulate electron-spin and magnetization to push forward cutting-edge spintronic technologies, like computing that mimics the human brain
 |
Abstract:
Our data-driven world demands more—more capacity, more efficiency, more computing power. To meet society’s insatiable need for electronic speed, physicists have been pushing the burgeoning field of spintronics.
‘Brand new physics’ for next generation spintronics: Physicists discover a unique quantum behavior that offers a new way to manipulate electron-spin and magnetization to push forward cutting-edge spintronic technologies, like computing that mimics the human brain
Salt Lake City, Utah | Posted on January 17th, 2025Traditional electronics use the charge of electrons to encode, store and transmit information. Spintronic devices utilize both the charge and spin-orientation of electrons. By assigning a value to electron spin (up=0 and down=1), spintronic devices offer ultra-fast, energy-efficient platforms.
To develop viable spintronics, physicists must understand the quantum properties within materials. One property, known as spin-torque, is crucial for the electrical manipulation of magnetization that’s required for the next generations of storage and processing technologies.
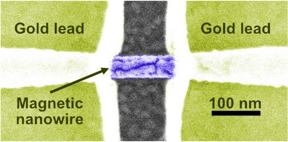
Researchers at the University of Utah and the University of California, Irvine (UCI), have discovered a new type of spin–orbit torque. The study that published in Nature Nanotechnology on Jan. 15, 2025, demonstrates a new way to manipulate spin and magnetization through electrical currents, a phenomenon that they’ve dubbed the anomalous Hall torque.
“This is brand new physics, which on its own is interesting, but there’s also a lot of potential new applications that go along with it,” said Eric Montoya, assistant professor of physics and astronomy at the University of Utah and lead author of the study. “These self-generated spin-torques are uniquely qualified for new types of computing like neuromorphic computing, an emerging system that mimics human brain networks.”
Hall of torques
Electrons have miniscule magnetic fields that, like planet Earth, are dipolar—some spins are oriented north (“up”) or south (“down”) or somewhere in between. Like magnets, opposite poles attract while like poles repel. Spin-orientation torque refers to the speed at which the electron spins around a fixed point.
In some materials, electricity will sort electrons based on their spin orientation. The distribution of spin-orientation, known as symmetry, will influence the material’s properties, such as the directional flow of a ferromagnet’s magnetic field.
Anomalous Hall torque is related to the well-known anomalous Hall effect, discovered by Edwin Hall in 1881. The anomalous Hall effect describes how electrons are scattered asymmetrically when they pass through a magnetic material, leading to a charge current that flows 90 degrees to the flow of an external electric current. It turns out, an analogous process occurs for spin—when an external electrical current is applied to a material, a spin current flows 90 degrees to the flow of electrical current with the spin-orientation along the direction of the magnetization.
“It really comes down to the symmetry. The different Hall effects describe the symmetry of how efficiently we can control the spin-orientation in a material,” Montoya said. “You can have one effect, or all effects in the same material. As material scientists, we can really tune these properties to get devices to do different things.”
A triad of torques for spintronic devices
The anomalous Hall torque is an example of an emerging concept in spintronics, known as self-generated spin–orbit torques, that exhibit unique spin-torque symmetries best equipped to support future spintronic devices. Together with the spin Hall torque and the recently identified planar Hall torque, also discovered by a team including coauthors Montoya and Ilya Krivorotov, physicist at UCI, the anomalous Hall torque completes a triad of Hall-like spin-orbit torques. Because the torque triad should be present in all conductive spintronic materials, the authors have coined them “Universal Hall torques.” Their universality will give researchers a powerful tool for developing spintronics devices.
Traditional spintronics usually consist of a non-magnetic layer sandwiched between two ferromagnetic materials, like in Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory (MRAM). Spin-torque MRAMs store and manipulate data by injecting a spin-polarized current from one magnetic layer into a second magnetic layer, which flips the spin-orientation of the second magnetic layer. The spin-orientation “up” or “down” can be mapped to the 0s and 1s used for binary data storage. Spin-torque MRAMs can store and access data faster and more efficiently than traditional MRAMS that rely on magnetic fields to flip the flow.
The authors demonstrate that in their device, the spin-orientation could be transferred from a ferromagnetic conductor to an adjacent non-magnetic material, eliminating the need for a second ferromagnetic layer. In fact, the authors built the first-ever spintronic prototype that exploits the anomalous Hall torque effect.
“We utilized anomalous Hall torque to create a nanoscale device known as a spin-torque oscillator. This device can mimic the functionality of a neuron, but is significantly smaller and operates at higher speeds,” said Krivorotov. “Our next step is to interconnect these devices into a larger network, enabling us to explore their potential for performing neuromorphic tasks, such as image recognition.”
*******
Xinyao Pei, physicist at UCI, was also a coauthor of the study. The National Science Foundation (ECCS-2213690 and DMREF-2324203) supported the research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Lisa Potter
University of Utah
Office: 801-585-3093
Cell: 949-533-7899
Expert Contact
Eric Montoya
University of Utah Department of Physics & Astronomy
Copyright © University of Utah
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








