Home > Press > Stanford scientists use nanotechnology to boost the performance of key industrial catalyst
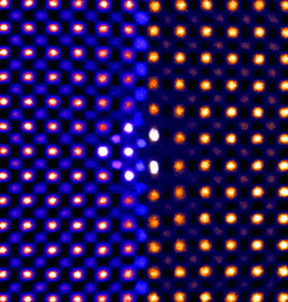 |
| This colorized transmission electron microscopy of ceria ultrathin film reveals that individual atoms (shown as dots) shift under intense pressure. CREDIT Sang?Chul?Lee |
Abstract:
A tiny amount of squeezing or stretching can produce a big boost in catalytic performance, according to a new study led by scientists at Stanford University and SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.
Stanford scientists use nanotechnology to boost the performance of key industrial catalyst
Stanford, CA | Posted on May 18th, 2017The discovery, published May 18 in Nature Communications, focuses on an industrial catalyst known as cerium oxide, or ceria, a spongy material commonly used in catalytic converters, self-cleaning ovens and various green-energy applications, such as fuel cells and solar water splitters.
"Ceria stores and releases oxygen as needed, like a sponge," said study co-author Will Chueh, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford and a faculty scientist at SLAC. "We discovered that stretching and compressing ceria by a few percent dramatically increases its oxygen storage capacity. This finding overturns conventional wisdom about oxide materials and could lead to better catalysts."
Catalytic converters
Ceria has long been used in catalytic converters to help remove air pollutants from vehicle exhaust systems.
"In your car, ceria grabs oxygen from poisonous nitrogen oxide, creating harmless nitrogen gas," said study lead author Chirranjeevi Balaji Gopal, a former postdoctoral researcher at Stanford. "Ceria then releases the stored oxygen and uses it to convert lethal carbon monoxide into benign carbon dioxide."
Studies have shown that squeezing and stretching ceria causes nanoscale changes that affect its ability to store oxygen.
"The oxygen storage capacity of ceria is critical to its effectiveness as a catalyst," said study co-author Aleksandra Vojvodic, a former staff scientist at SLAC now at the University of Pennsylvania, who led the computational aspect of this work. "The theoretical expectation based on previous studies is that stretching ceria would increase its capacity to store oxygen, while compressing would lower its storage capacity."
To test this prediction, the research team grew ultrathin films of ceria, each just a few nanometers thick, on top of substrates made of different materials. This process subjected the ceria to stress equal to 10,000 times the Earth's atmosphere. This enormous stress caused the molecules of ceria to separate and squeeze together a distance of less than one nanometer.
Surprise results
Typically, materials like ceria relieve stress by forming defects in the film. But atomic-scale analysis revealed a surprise.
"Using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy to resolve the position of individual atoms, we showed that the films remain stretched or compressed without forming such defects, allowing the stress to remain in full force," said Robert Sinclair, a professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford.
To measure the impact of stress under real-world operating conditions, the researchers analyzed the ceria samples using the brilliant beams of X-ray light produced at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory's Advanced Light Source.
The results were even more surprising.
"We discovered that the strained films exhibited a fourfold increase in the oxygen storage capacity of ceria," Gopal said. "It doesn't matter if you stretch it or compress it. You get a remarkably similar increase."
The high-stress technique used by the research team is readily achievable through nanoengineering, Chueh added.
"This discovery has significant implications on how to nanoengineer oxide materials to improve catalytic efficiency for energy conversion and storage," he said. "It's important for developing solid oxide fuel cells and other green-energy technologies, including new ways to make clean fuels from carbon dioxide or water."
###
Other Stanford co-authors of the study are Max Garcia-Melchor, now at Trinity College Dublin (Ireland), and graduate students Sang Chul Lee, Zixuan Guan, Yezhou Shi and Matteo Monti. Additional co-authors are Andrey Shavorskiy of Lund University (Sweden) and Hendrik Bluhm of Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mark Shwartz
650-723-9296
Copyright © Stanford University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








