Home > Press > Nano-chimneys can cool circuits: Rice University scientists calculate tweaks to graphene would form phonon-friendly cones
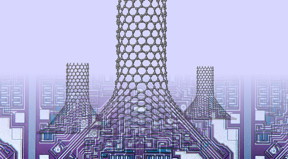 |
| Simulations by Rice University scientists show that placing cones between graphene and carbon nanotubes could enhance heat dissipation from nano-electronics. The nano-chimneys become better at conducting heat-carrying phonons by spreading out the number of heptagons required by the graphene-to-nanotube transition. Credit: Alex Kutana/Rice University |
Abstract:
A few nanoscale adjustments may be all that is required to make graphene-nanotube junctions excel at transferring heat, according to Rice University scientists.
Nano-chimneys can cool circuits: Rice University scientists calculate tweaks to graphene would form phonon-friendly cones
Houston, TX | Posted on January 4th, 2017The Rice lab of theoretical physicist Boris Yakobson found that putting a cone-like "chimney" between the graphene and nanotube all but eliminates a barrier that blocks heat from escaping.
The research appears in the American Chemical Society's Journal of Physical Chemistry C.
Heat is transferred through phonons, quasiparticle waves that also transmit sound. The Rice theory offers a strategy to channel damaging heat away from next-generation nano-electronics.
Both graphene and carbon nanotubes consist of six-atom rings, which create a chicken-wire appearance, and both excel at the rapid transfer of electricity and phonons.
But when a nanotube grows from graphene, atoms facilitate the turn by forming heptagonal (seven-member) rings instead. Scientists have determined that forests of nanotubes grown from graphene are excellent for storing hydrogen for energy applications, but in electronics, the heptagons scatter phonons and hinder the escape of heat through the pillars.
The Rice researchers discovered through computer simulations that removing atoms here and there from the two-dimensional graphene base would force a cone to form between the graphene and the nanotube. The geometric properties (aka topology) of the graphene-to-cone and cone-to-nanotube transitions require the same total number of heptagons, but they are more sparsely spaced and leave a clear path of hexagons available for heat to race up the chimney.
"Our interest in advancing new applications for low-dimensional carbon -- fullerenes, nanotubes and graphene -- is broad," Yakobson said. "One way is to use them as building blocks to fill three-dimensional spaces with different designs, creating anisotropic, nonuniform scaffolds with properties that none of the current bulk materials have. In this case, we studied a combination of nanotubes and graphene, connected by cones, motivated by seeing such shapes obtained in our colleagues' experimental labs."
The researchers tested phonon conduction through simulations of free-standing nanotubes, pillared graphene and nano-chimneys with a cone radius of either 20 or 40 angstroms. The pillared graphene was 20 percent less conductive than plain nanotubes. The 20-angstrom nano-chimneys were just as conductive as plain nanotubes, while 40-angstrom cones were 20 percent better than the nanotubes.
"The tunability of such structures is virtually limitless, stemming from the vast combinatorial possibilities of arranging the elementary modules," said Alex Kutana, a Rice research scientist and co-author of the study. "The actual challenge is to find the most useful structures given a vast number of possibilities and then make them in the lab reliably.
"In the present case, the fine-tuning parameters could be cone shapes and radii, nanotube spacing, lengths and diameters. Interestingly, the nano-chimneys also act like thermal diodes, with heat flowing faster in one direction than the other," he said.
Rice graduate student Ziang Zhang is lead author of the paper. Ajit Roy, a principal materials research engineer at the Air Force Research Laboratory in Dayton, Ohio, is a co-author. Yakobson is the Karl F. Hasselmann Professor of Materials Science and NanoEngineering and a professor of chemistry.
The Air Force Office of Scientific Research and its Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative supported the research. Calculations were performed on Rice’s National Science Foundation-supported DAVinCI supercomputer administered by the Center for Research Computing, procured in partnership with the Ken Kennedy Institute for Information Technology.
-30-
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,910 undergraduates and 2,809 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for happiest students and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to http://tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview .
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Rice University Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
Rice University Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








