Home > Press > UT Dallas nanotechnology research leads to super-elastic conducting fibers
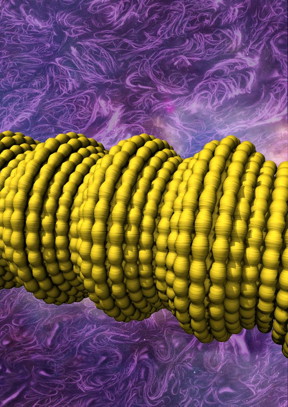 |
| University of Texas at Dallas scientists have constructed novel fibers by wrapping sheets of tiny carbon nanotubes to form a sheath around a long rubber core. This illustration shows complex two-dimensional buckling, shown in yellow, of the carbon nanotube sheath/rubber-core fiber. The buckling results in a conductive fiber with super elasticity and novel electronic properties. CREDIT: UT Dallas Alan G. MacDiarmid NanoTech Institute |
Abstract:
An international research team based at The University of Texas at Dallas has made electrically conducting fibers that can be reversibly stretched to over 14 times their initial length and whose electrical conductivity increases 200-fold when stretched.
UT Dallas nanotechnology research leads to super-elastic conducting fibers
Dallas, TX | Posted on July 24th, 2015The research team is using the new fibers to make artificial muscles, as well as capacitors whose energy storage capacity increases about tenfold when the fibers are stretched. Fibers and cables derived from the invention might one day be used as interconnects for super-elastic electronic circuits; robots and exoskeletons having great reach; morphing aircraft; giant-range strain sensors; failure-free pacemaker leads; and super-stretchy charger cords for electronic devices.
In a study published in the July 24 issue of the journal Science, the scientists describe how they constructed the fibers by wrapping lighter-than-air, electrically conductive sheets of tiny carbon nanotubes to form a jelly-roll-like sheath around a long rubber core.
The new fibers differ from conventional materials in several ways. For example, when conventional fibers are stretched, the resulting increase in length and decrease in cross-sectional area restricts the flow of electrons through the material. But even a "giant" stretch of the new conducting sheath-core fibers causes little change in their electrical resistance, said Dr. Ray Baughman, senior author of the paper and director of the Alan G. MacDiarmid NanoTech Institute at UT Dallas.
One key to the performance of the new conducting elastic fibers is the introduction of buckling into the carbon nanotube sheets. Because the rubber core is stretched along its length as the sheets are being wrapped around it, when the wrapped rubber relaxes, the carbon nanofibers form a complex buckled structure, which allows for repeated stretching of the fiber.
"Think of the buckling that occurs when an accordion is compressed, which makes the inelastic material of the accordion stretchable," said Baughman, the Robert A. Welch Distinguished Chair in Chemistry at UT Dallas.
"We make the inelastic carbon nanotube sheaths of our sheath-core fibers super stretchable by modulating large buckles with small buckles, so that the elongation of both buckle types can contribute to elasticity. These amazing fibers maintain the same electrical resistance, even when stretched by giant amounts, because electrons can travel over such a hierarchically buckled sheath as easily as they can traverse a straight sheath."
Dr. Zunfeng Liu, lead author of the study and a research associate in the NanoTech Institute, said the structure of the sheath-core fibers "has further interesting and important complexity." Buckles form not only along the fiber's length, but also around its circumference.
"Shrinking the fiber's circumference during fiber stretch causes this second type of reversible hierarchical buckling around its circumference, even as the buckling in the fiber direction temporarily disappears," Liu said. "This novel combination of buckling in two dimensions avoids misalignment of nanotube and rubber core directions, enabling the electrical resistance of the sheath-core fiber to be insensitive to stretch."
By adding a thin overcoat of rubber to the sheath-core fibers and then another carbon nanotube sheath, the researchers made strain sensors and artificial muscles in which the buckled nanotube sheaths serve as electrodes and the thin rubber layer is a dielectric, resulting in a fiber capacitor. These fiber capacitors exhibited a capacitance change of 860 percent when the fiber was stretched 950 percent.
"No presently available material-based strain sensor can operate over nearly as large a strain range," Liu said.
Adding twist to these double-sheath fibers resulted in fast, electrically powered torsional -- or rotating -- artificial muscles that could be used to rotate mirrors in optical circuits or pump liquids in miniature devices used for chemical analysis, said Dr. Carter Haines BS'11, PhD'15, a research associate in the NanoTech Institute and an author of the paper.
In the laboratory, Nan Jiang, a research associate in the NanoTech Institute, demonstrated that the conducting elastomers can be fabricated in diameters ranging from the very small -- about 150 microns, or twice the width of a human hair -- to much larger sizes, depending on the size of the rubber core. "Individual small fibers also can be combined into large bundles and plied together like yarn or rope," she said.
"This technology could be well-suited for rapid commercialization," said Dr. Raquel Ovalle-Robles MS'06 PhD'08, an author on the paper and chief research and intellectual properties strategist at Lintec of America's Nano-Science & Technology Center.
"The rubber cores used for these sheath-core fibers are inexpensive and readily available," she said. "The only exotic component is the carbon nanotube aerogel sheet used for the fiber sheath."
Last year, UT Dallas licensed to Lintec of America a process Baughman's team developed to transform carbon nanotubes into large-scale structures, such as sheets. Lintec opened its Nano-Science & Technology Center in Richardson, Texas, less than 5 miles from the UT Dallas campus, to manufacture carbon nanotube aerogel sheets for diverse applications.
###
The Science research was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the Robert A. Welch Foundation, the U.S. Army, the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation and the Office of Naval Research. Several funding sources from China and Brazil also contributed.
In addition to Baughman, Liu, Haines, Jiang and Ovalle-Robles, paper authors based at UT Dallas' NanoTech Institute are research scientists Dr. Shaoli Fang and Dr. Marcio Lima, and research associates Dr. Xavier Lepro and Dr. Jiangtao Di. Contributors based in the UT Dallas Department of Mechanical Engineering include Dr. Hongbing Lu, professor; Dr. Dong Qian, associate professor; and Xuemin Wang, research assistant. Researchers also contributed from universities in Florida, China and Brazil.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Amanda Siegfried
972-883-4335
Copyright © University of Texas at Dallas
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Robotics
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
![]() Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Aerogels
![]() The lightest shielding material in the world: Protection against electromagnetic interference July 3rd, 2020
The lightest shielding material in the world: Protection against electromagnetic interference July 3rd, 2020
![]() Super-light, super-insulating ceramic aerogel keeps the hottest temperatures at bay February 17th, 2019
Super-light, super-insulating ceramic aerogel keeps the hottest temperatures at bay February 17th, 2019
![]() Researchers reduce expensive noble metals for fuel cell reactions August 22nd, 2016
Researchers reduce expensive noble metals for fuel cell reactions August 22nd, 2016
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








