Home > Press > Scientists use blur to sharpen DNA mapping: Rice University researchers transcend optical limits to locate specific sequences
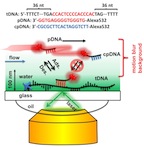 |
| A super-resolution technique developed at Rice University allows fluorescent-labeled probe DNA to pinpoint target DNA sequences in an immobilized strand in ways neither regular nor electron microscopes are able. The technique relies on multiple images of probes binding temporarily to targets as they flow over the strand and are captured by a camera. Credit: Landes Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
With high-tech optical tools and sophisticated mathematics, Rice University researchers have found a way to pinpoint the location of specific sequences along single strands of DNA, a technique that could someday help diagnose genetic diseases.
Scientists use blur to sharpen DNA mapping: Rice University researchers transcend optical limits to locate specific sequences
Houston, TX | Posted on October 9th, 2013Proof-of-concept experiments in the Rice lab of chemist Christy Landes identified DNA sequences as short as 50 nucleotides at room temperature, a feat she said is impossible with standard microscopes that cannot see targets that small, or electron microscopes that require targets to be in a vacuum or cryogenically frozen.
The technique called "super-localization microscopy" has been known for a while, Landes said, but its application in biosensing is just beginning.
The work by Landes, Rice postdoctoral associate Jixin Chen and undergraduate student Alberto Bremauntz is detailed in the American Chemical Society journal Applied Materials and Interfaces.
The Rice researchers call their super-resolution technique "motion blur point accumulation for imaging in nanoscale topography" (mbPAINT). With it, they resolved structures as small as 30 nanometers (billionths of a meter) by making, essentially, a movie of fluorescent DNA probes flowing over a known target sequence along an immobilized single strand of DNA.
The probes are labeled with a fluorescent dye that lights up only when attached to the target DNA. In the experimental setup, most would flow by unseen, but some would bind to the target for a few milliseconds, just long enough to be captured by the camera before the moving liquid pulled them away. Processing images of these brief events amidst the background blur allows the researchers to image objects smaller than the natural diffraction limits of light-based imaging, which do not allow for the resolution of targets smaller than the wavelength of light used to illuminate them.
Even the Landes lab's system is subject to these physical limitations. Individual images of fluorescing probes on targets are just a pixelated blur. But it's a blur with a bright spot, and careful analysis of multiple images allows the researchers to pinpoint that spot along the strand.
"The probes are moving so fast that in real time, all we would see with the camera is a line," Chen said. But when the camera firing at 30-millisecond intervals happened to catch a bound probe, it clearly stood out. The probes sometime picked out two sequences along a strand that would have been seen as a single blur via regular fluorescent microscopy.
Landes said one goal for mbPAINT is to map ever-smaller fragments of DNA. "Eventually, we'd like to get down to a couple of nucleotides," she said. "Some diseases are characterized by one amino acid mutation, which is three nucleotides, and there are many diseases associated with very small genetic mutations that we'd like to be able to identify.
"We're thinking this method will be ideally suited for diseases associated with small, localized mutations that are not possible to detect in any other inexpensive way," she said.
Landes sees mpPAINT as not only more cost-effective but also able to capture information electron microscopes cannot.
"One of the reasons people invented electron microscopy is to image objects smaller than light's diffraction limit, because biomolecules such as proteins and DNAs are smaller than that," she said. "But electron microscopy requires cryogenic temperatures or a vacuum. You can't easily watch things react in solution.
"The advent of this technology allows us to see the biological processes of nano-sized objects as they happen in water, with buffers and salts, at room temperature, at body temperature or even in a cell. It's very exciting," Landes said.
Rice graduate students Lydia Kisley and Bo Shaung are co-authors of the paper.
The National Science Foundation, the Welch Foundation and the National Institutes of Health supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,708 undergraduates and 2,374 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to tinyurl.com/AboutRiceU.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Tools
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








