Home > Press > Researchers Create Semiconductor ‘Nano-Shish-Kebabs’ With Potential for 3-D Technologies
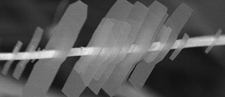 |
| The "shish-kebab" consists of two-dimensional nanosheets strung along a nanowire. |
Abstract:
"Epitaxial Nanosheet-Nanowire Heterostructures"
Authors: Chun Li, Yifei Yu and Linyou Cao, North Carolina State University; Miaofang Chi, Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Published: online Feb. 18 in Nano Letters
Abstract: We demonstrate synthesis of a new type of heterostructures that comprise two-dimensional (2D) nanosheets (NSs) epitaxially grown at one-dimensional (1D) nanowires (NWs). The synthesis involves using materials with a graphite-like layered structure in which covalently bonded layers are held by weak van der Waals forces. GeS was used as a prototype material in this work. The synthesis also involves a seeded-growth process, where GeS NWs are grown first as seeds followed by a seeded growth of NSs at the pre-grown NWs. We observe that exposing the pre-grown NWs to air prior to the seeded growth is critical for the formation of NSs to yield NS?NW heterostructures. Our experimental results suggest that this might be due to a mild oxidation caused by the air exposure at the NW surface, which could subsequently facilitate the nucleation of NSs at the NWs. It also suggests that the surface oxidation needs to be controlled in a proper range in order to achieve optimized NS growths. We believe that this synthetic strategy may generally apply to the growth of NS?NW heterostructures of other layered chalcogenide materials. NS?NW heterostructures provide capabilities to monolithically integrate the functionality of 1D NWs and 2D NSs into a 3D space. It holds great potential in applications that request complex nanomaterials with multiple functionality, high surface area, and efficient charge transport, such as energy storage, chemical sensing, solar energy conversion, and 3D electric and photonic devices.
Researchers Create Semiconductor ‘Nano-Shish-Kebabs’ With Potential for 3-D Technologies
Raleigh, NC | Posted on February 19th, 2013Researchers at North Carolina State University have developed a new type of nanoscale structure that resembles a "nano-shish-kebab," consisting of multiple two-dimensional nanosheets that appear to be impaled upon a one-dimensional nanowire. However, the nanowire and nanosheets are actually a single, three-dimensional structure consisting of a seamless series of germanium sulfide (GeS) crystals. The structure holds promise for use in the creation of new, three-dimensional (3-D) technologies.
The researchers believe this is the first engineered nanomaterial to combine one-dimensional and two-dimensional structures in which all of the components have a shared crystalline structure.
Combining the nanowire and nanosheets into a single "heterostructure" creates a material with both a large surface area and - because GeS is a semiconductor - the ability to transfer electric charges efficiently. The nanosheets provide a very large surface area, and the nanowire acts as a channel that can transmit charges between the nanosheets or from the nanosheets to another surface. This combination of features means it could be used to develop 3-D devices, such as next-generation sensors, photodetectors or solar cells. This 3-D structure could also be useful for developing new energy storage technologies, such as next-generation supercapacitors.
"We think this approach could also be used to create heterostructures like these using other materials whose molecules form similar crystalline layers, such as molybdenum sulfide (MoS2)," says Dr. Linyou Cao, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and co-author of a paper on the research. "And, while germanium sulfide has excellent photonic properties, MoS2 holds more promise for electronic applications."
The process, Cao says, is also attractive because "it is inexpensive and could be scaled up for industrial processes."
To create the nano-shish-kebabs, the researchers begin by creating a GeS nanowire approximately 100 nanometers in width. The nanowire is then exposed to air, creating nucleation sites on the wire surface through weak oxidation. The nanowire is then exposed to GeS vapor, which forms into two-dimensional nanosheets at each of the nucleation sites.
"Our next step is to see if we can create these heterostructures in other materials, such as MoS2," Cao says. "We think we can, but we need to prove it."
The paper, "Epitaxial Nanosheet-Nanowire Heterostructures," was published online Feb. 18 in Nano Letters. The lead author is Dr. Chun Li, a former postdoctoral researcher at NC State. Co-authors are Yifei Yu, a Ph.D. student at NC State; Cao; and Dr. Miaofang Chi of Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The research was supported by the U.S. Army Research Office.
-shipman-
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Dr. Linyou Cao
919.515.5407
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








