Home > Press > Physicists cross hurdle in quantum manipulation of matter
 |
Abstract:
Team successfully decoupled a single quantum spin from its surroundings
Physicists cross hurdle in quantum manipulation of matter
Ames, IA | Posted on September 21st, 2010Finding ways to control matter at the level of single atoms and electrons fascinates many scientists and engineers because the ability to manipulate single charges and single magnetic moments (spins) may help researchers penetrate deep into the mysteries of quantum mechanics and modern solid-state physics. It may also allow development of new, highly sensitive magnetometers with nanometer resolution, single-spin transistors for coherent spintronics, and solid-state devices for quantum information processing.
Recently, a collaboration of experimentalists from the Kavli Institute of Nanosciences at Delft University of Technology and theorists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory made a breakthrough in the area of controlling single quantum spins. The results were published in Science Express on Sept. 9.
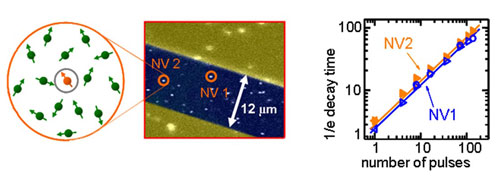
The researchers developed and implemented a special kind of quantum control over a single quantum magnetic moment (spin) of an atomic-sized impurity in diamond. These impurities, called nitrogen-vacancy (or N-V) centers, have attracted much attention due to their unusual magnetic and optical properties. But their fragile quantum states are easily destroyed by even miniscule interactions with the outside world.
By applying a specially designed sequence of high-precision electromagnetic pulses, the scientists were able to protect the arbitrary quantum state of a single spin, and they made the spin evolve as if it was completely decoupled from the outside world. In this way, scientists achieved a 25-fold increase in the lifetime of the quantum spin state at room temperature. This is the first demonstration of a universal dynamical decoupling realized on a single solid state quantum spin.
"Uncontrolled interactions of the spins with the environment have been the major hurdle for implementing quantum technologies" said the leader of Dutch experimental group, associate professor Ronald Hanson from Kavli Institute of Nanoscience at Delft. "Our results demonstrate that this hurdle can be overcome by advanced control of the spin itself."
"Implementing dynamical decoupling on a single quantum spin in solid state at room temperature has been an appealing but distant goal for quite a while. In the meantime, much theoretical and experimental knowledge has been accumulated in the community," added Viatcheslav Dobrovitski, who led the theoretical research effort at the Ames Laboratory. "We used this knowledge to design our pulse sequences, and the collaboration between theory and experiment greatly helped us in this work."
Besides its importance to fundamental understanding of quantum mechanics, the team's achievement opens a way to using the impurity centers in diamond as highly sensitive nanoscale magnetic sensors, and potentially, as qubits for larger-scale quantum information processing.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Viatcheslav Dobrovitski, USDOE's Ames Laboratory,
+1-515-294-8666
Ronald Hanson, Kavli Institute of Nanosciences at Delft University of Technology,
+31-15-2787188
Breehan Gerleman Lucchesi, USDOE’s Ames Laboratory Public Affairs,
+1-515-294-9750
Copyright © Ames Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








