Home > Press > Behind the Secrets of Silk Lie High-Tech Opportunities
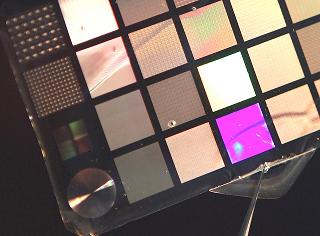 |
| Using biocompatible green processing, silk cocoons can yield a pure silk protein with numerous applications in fields such as medicine and electronics. The silk card above shows diffractive optics entirely constituted by pure silk obtained by pouring silk solution on nanopatterned molds and letting the solution dry and crystallize. The resulting film retains the pattern and is a free-standing optical component so flexible it can be rolled up. (Fiorenzo Omenetto/Tufts University) |
Abstract:
A Decade of Research Yields New Uses for Ancient Material
Behind the Secrets of Silk Lie High-Tech Opportunities
Medford/Somerville, MA | Posted on July 31st, 2010Tougher than a bullet-proof vest yet synonymous with beauty and luxury, silk fibers are a masterpiece of nature whose remarkable properties have yet to be fully replicated in the laboratory.
Thanks to their amazing mechanical properties as well as their looks, silk fibers have been important materials in textiles, medical sutures, and even armor for 5,000 years.
Silk spun by spiders and silk worms combines high strength and extensibility. This one-two punch is unmatched by synthetics, even though silk is made from a relatively simple protein processed from water.
But in recent years scientists have begun to unravel the secrets of silk.
In the July 30, 2010, issue of the journal Science, Tufts biomedical engineering researchers Fiorenzo Omenetto, Ph.D., and David Kaplan, Ph.D., report that "Silk-based materials have been transformed in just the past decade from the commodity textile world to a growing web of applications in more high technology directions."
Fundamental discoveries into how silk fibers are made have shown that chemistry, molecular biology and biophysics all play a role in the process. These discoveries have provided the basis for a new generation of applications for silk materials, from medical devices and drug delivery to electronics.
Edible Optics, Implantable Electronics
The Science paper notes that the development of silk hydrogels, films, fibers and sponges is making possible advances in photonics and optics, nanotechnology, electronics, adhesives and microfluidics, as well as engineering of bone and ligaments. Because silk fiber formation does not rely on complex or toxic chemistries, such materials are biologically and environmentally friendly, even able to integrate with living systems.
Down the silk road of the future, Kaplan and Omenetto believe applications could include degradable and flexible electronic displays for sensors that are biologically and environmentally compatible and implantable optical systems for diagnosis and treatment. Progress in "edible optics" and implantable electronics has already been demonstrated by Kaplan and Omenetto, John Rogers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and others.
Many challenges remain. Kaplan and Omenetto say that key questions include how to fully replicate native silk assembly in the lab, how best to mimic silk protein sequences via genetic engineering to scale-up materials production, and how to use silk as a model polymer to spur new synthetic polymer designs that mimic natural silk's green chemistry.
Techniques for reprocessing natural silk protein in the lab continue to advance. Silks are also being cloned and expressed in a variety of hosts, including E. coli bacteria, fungi, plants and mammals, and through transgenic silkworms.
One day, efficient transgenic plants could be used to crop silk in much the same way that cotton is harvested today, the Tufts researchers note in their paper. In some regions, silk production might create a new microeconomy, as demand grows and production techniques improve.
"Based on the recent and rapid progression of silk materials from the ancient textile use into a host of new high-technology applications, we anticipate growth in the use of silks in a wide platform of applications will continue as answers to these remaining questions are obtained," say Omenetto and Kaplan.
Kaplan is chair of the Biomedical Engineering Department at Tufts School of Engineering and the Stern Family Professor in Engineering. He also directs the NIH Tissue Engineering Resource Center that involves Tufts and Columbia University. His work lies at the interface between biology and materials science and engineering, and he has been studying novel biomaterials, many of them silk-based, for 30 years. Professor of Biomedical Engineering Fiorenzo Omenetto is a frequent collaborator with Kaplan who has pioneered silk optics and use of silk as a green material for photonics and other high tech applications.
Support for this research on silk comes from the National Institutes of Health, National Science Foundation, Air Force Office of Science Research and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency.
####
About Tufts University
Tufts University, located on three Massachusetts campuses in Boston, Medford/Somerville, and Grafton, and in Talloires, France, is recognized among the premier research universities in the United States. Tufts enjoys a global reputation for academic excellence and for the preparation of students as leaders in a wide range of professions. A growing number of innovative teaching and research initiatives span all Tufts campuses, and collaboration among the faculty and students in the undergraduate, graduate and professional programs across the university's schools is widely encouraged.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kim Thurler
617-627-3175
Copyright © Tufts University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Microfluidics/Nanofluidics
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








