Home > Press > Thorium superconductivity: Scientists discover a new high-temperature superconductor
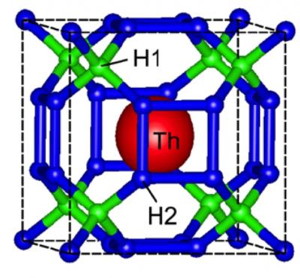 |
| This is the crystal structure of ThH10. CREDIT Dmitry V.Semenok et al., Materials Today |
Abstract:
A group of scientists led by Artem Oganov, Professor at Skoltech and MIPT, and Dr. Ivan Troyan at the Institute of Crystallography of RAS have succeeded in synthesizing thorium decahydride (ThH10), a new superconducting material with a very high critical temperature (161 K). The results of their study supported by a Russian Science Foundation (RSF) grant were published in the journal Materials Today.
Thorium superconductivity: Scientists discover a new high-temperature superconductor
Moscow, Russia | Posted on November 8th, 2019A truly remarkable property of quantum materials, superconductivity is a complete loss of electrical resistance under quite particular, and sometimes, very harsh conditions. Despite the tremendous potential for quantum computers and high-sensitivity detectors, the application of quantum materials is hindered by the fact that superconductivity typically manifests itself at very low temperatures or extremely high pressures. Until recently, the list of superconductors was topped by mercury-containing cuprate that becomes superconducting at 135 K (-138 °C). This year, lanthanum decahydride, LaH10, has set a new record of -13 oС, which is very close to room temperature, although in the case of LaH10 superconductivity is achieved at nearly 2 million atmospheres, a pressure that can hardly be attained in real life. It is important to achieve superconductivity at temperatures and pressures close to room levels. In 2018, Alexander Kvashnin, a research scientist at the lab directed by Skoltech and MIPT professor, Artem R. Oganov, predicted a new material, thorium polyhydride (ThH10), with a critical temperature of -32 oС at THE pressure of 1 million atmospheres.
In their recent study, scientists from the Institute of Crystallography of RAS, Skoltech, MIPT and the Lebedev Institute of Physics of RAS have successfully obtained ThH10 and studied its transport properties and superconductivity. Their findings corroborated the theoretical predictions, proving that ThH10 exists at pressures above 0.85 million atmospheres and displays outstanding high-temperature superconducting performance. The scientists could only determine the critical temperature at 1.7 million atmospheres and found it to be -112 oС, which is consistent with the theoretical prediction for this pressure value, placing ThH10 among the record-breaking high-temperature superconductors.
"Modern theory, and in particular, the USPEX method developed by myself and my students, yet again displayed their amazing predictive power. ThH10 pushes the boundaries of classical chemistry and possesses unique properties that were predicted theoretically and recently confirmed by experiment. Most notably, the experimental results obtained by Ivan Troyan's lab are of very high quality," says Artem R. Oganov, co-director of the study and professor at Skoltech and MIPT.
"We discovered that superconductivity predicted in theory does exist at -112 oС and 1.7 million atmospheres. Given the strong consistency between theory and experiment, it would be interesting to check whether ThH10 will show superconductivity at up to -30-40 °C and lower pressures as predicted," says co-director of the study, Dr. Ivan Troyan.
"Thorium hydride is just one of the elements in a large and rapidly growing class of hydride superconductors. I believe that in the coming years, hydride superconductivity will expand beyond the cryogenic range to find application in the design of electronic devices," says the first author of the study and Skoltech PhD student, Dmitry Semenok.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Alina Chernova
890-556-53633
Copyright © Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (Skoltech)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








