Home > Press > Better microring sensors for optical applications
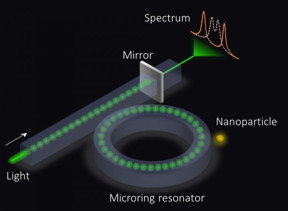 |
| An exceptional surface-based sensor. The microring resonator is coupled to a waveguide with an end mirror that partially reflects light, which in turn enhances the sensitivity. CREDIT Ramy El-Ganainy and Qi Zhong |
Abstract:
Optical sensing is one of the most important applications of light science. It plays crucial roles in astronomy, environmental science, industry and medical diagnoses.
Better microring sensors for optical applications
Houghton, MI | Posted on May 10th, 2019Despite the variety of schemes used for optical sensing, they all share the same principle: The quantity to be measured must leave a "fingerprint" on the optical response of the system. The fingerprint can be its transmission, reflection or absorption. The stronger these effects are, the stronger the response of the system.
While this works well at the macroscopic level, measuring tiny, microscopic quantities that induce weak response is a challenging task. Researchers have developed techniques to overcome this difficulty and improve the sensitivity of their devices. Some of these techniques, which rely on complex quantum optics concepts and implementations, have indeed proved useful, such as in sensing gravitational waves in the LIGO project. Others, which are based on trapping light in tiny boxes called optical resonators, have succeeded in detecting micro-particles and relatively large biological components.
Nonetheless, the ability to detect small nano-particles and eventually single molecules remains a challenge. Current attempts focus on a special type of light trapping devices called microring or microtoroid resonators -- these enhance the interaction between light and the molecule to be detected. The sensitivity of these devices, however, is limited by their fundamental physics.
In their article "Sensing with Exceptional Surfaces in Order to Combine Sensitivity with Robustness" published in Physical Review Letters (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.153902), physicists and engineers from Michigan Technological University, Pennsylvania State University and the University of Central Florida propose a new type of sensor. They are based on the new notion of exceptional surfaces: surfaces that consist of exceptional points.
Exceptional Points for Exceptionally Sensitive Detection
In order to understand the meaning of exceptional points, consider an imaginary violin with only two strings. In general, such a violin can produce just two different tones -- a situation that corresponds to a conventional optical resonator. If the vibration of one string can alter the vibration of the other string in a way that the sound and the elastic oscillations create only one tone and one collective string motion, the system has an exceptional point.
A physical system that exhibits an exceptional point is very fragile. In other words, any small perturbation will dramatically alter its behavior. The feature makes the system highly sensitive to tiny signals.
"Despite this promise, the same enhanced sensitivity of exceptional point-based sensors is also their Achilles heel: These devices are very sensitive to unavoidable fabrication errors and undesired environmental variations," said Ramy El-Ganainy, associate professor of physics, adding that the sensitivity necessitated clever tuning tricks in previous experimental demonstrations.
"Our current proposal alleviates most of these problems by introducing a new system that has the same enhanced sensitivity reported in previous work, while at the same time robust against the majority of the uncontrivable experimental uncertainty," said Qi Zhong, lead author on the paper and a graduate student who is currently working towards his doctorate degree at Michigan Tech.
Though the design of microring sensors continues to be refined, researchers are hopeful that by improving the devices, seemingly tiny optical observations will have large effects.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kelley Christensen
906-231-9168
Copyright © Michigan Technological University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








