Home > Press > Hematene joins parade of new 2D materials: Rice University-led team extracts 3-atom-thick sheets from common iron oxide
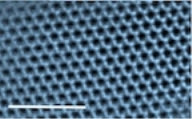 |
| Hematene created by a Rice University-led team is the first known two-dimensional non-van der Waals material. The transmission electron image shows a single sheet of hematene. Scale bar equals 0.5 microns. (Credit: Shyam Sinha and Peter van Aken/Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research, Stuttgart, Germany) |
Abstract:
In the wake of its recent discovery of a flat form of gallium, an international team led by scientists from Rice University has created another two-dimensional material that the researchers said could be a game changer for solar fuel generation.
Hematene joins parade of new 2D materials: Rice University-led team extracts 3-atom-thick sheets from common iron oxide
Houston, TX | Posted on May 8th, 2018Rice materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan and colleagues extracted 3-atom-thick hematene from common iron ore. The research was introduced in a paper today in Nature Nanotechnology.
Hematene may be an efficient photocatalyst, especially for splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen, and could also serve as an ultrathin magnetic material for spintronic-based devices, the researchers said.
"2D magnetism is becoming a very exciting field with recent advances in synthesizing such materials, but the synthesis techniques are complex and the materials' stability is limited," Ajayan said. "Here, we have a simple, scalable method, and the hematene structure should be environmentally stable."
Ajayan's lab worked with researchers at the University of Houston and in India, Brazil, Germany and elsewhere to exfoliate the material from naturally occurring hematite using a combination of sonication, centrifugation and vacuum-assisted filtration.
Hematite was already known to have photocatalytic properties, but they are not good enough to be useful, the researchers said.
"For a material to be an efficient photocatalyst, it should absorb the visible part of sunlight, generate electrical charges and transport them to the surface of the material to carry out the desired reaction," said Oomman Varghese, a co-author and associate professor of physics at the University of Houston.
"Hematite absorbs sunlight from ultraviolet to the yellow-orange region, but the charges produced are very short-lived. As a result, they become extinct before they reach the surface," he said.
Hematene photocatalysis is more efficient because photons generate negative and positive charges within a few atoms of the surface, the researchers said. By pairing the new material with titanium dioxide nanotube arrays, which provide an easy pathway for electrons to leave the hematene, the scientists found they could allow more visible light to be absorbed.
The researchers also discovered that hematene's magnetic properties differ from those of hematite. While native hematite is antiferromagnetic, tests showed that hematene is ferromagnetic, like a common magnet. In ferromagnets, atoms' magnetic moments point in the same direction. In antiferromagnets, the moments in adjacent atoms alternate.
Unlike carbon and its 2D form, graphene, hematite is a non-van der Waals material, meaning it's held together by 3D bonding networks rather than non-chemical and comparatively weaker atomic van der Waals interactions.
"Most 2D materials to date have been derived from bulk counterparts that are layered in nature and generally known as van der Waals solids," said co-author Professor Anantharaman Malie Madom Ramaswamy Iyer of the Cochin University of Science and Technology, India. "2D materials from bulk precursors having (non-van der Waals) 3D bonding networks are rare, and in this context hematene assumes great significance."
According to co-author Chandra Sekhar Tiwary, a former postdoctoral researcher at Rice and now an assistant professor at the Indian Institute of Technology, Gandhinagar, the collaborators are exploring other non-van der Waals materials for their 2D potential.
Iyer and Rice visiting student Aravind Puthirath Balan of Cochin University are lead authors of the study. Co-authors are Sruthi Radhakrishnan, Amey Apte, Carlos de los Reyes, Vidya Kochat, Robert Vajtai, Angel Martí and Gelu Costin of Rice; Cristiano Woellner and Douglas Galvao of the State University of Campinas, Brazil; Shyam Sinha and Peter van Aken of the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research, Stuttgart, Germany; Liangzi Deng, Banki Manmadha Rao, Maggie Paulose and Ram Neupane of the University of Houston, Ching-Wu Chu of the University of Houston and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, Calif.; and Avetik Harutyunyan of the Honda Research Institute USA Inc., Columbus, Ohio.
Ajayan is chair of Rice's Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering, the Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Engineering and a professor of chemistry.
The research was supported by India's Ministry of Human Resource Development, the U.S. Army Research Office Multidisciplinary Research Institute, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the São Paulo Research Foundation, the T.L.L. Temple Foundation, the John J. and Rebecca Moores Endowment, the State of Texas, Shell International Exploration and Production Inc. and the Neutrino Observatory.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,970 undergraduates and 2,934 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction and No. 2 for happiest students by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to http://tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview .
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
![]() George R. Brown School of Engineering:
George R. Brown School of Engineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








