Home > Press > Magnetized viruses attack harmful bacteria: Rice, China team uses phage-enhanced nanoparticles to kill bacteria that foul water treatment systems
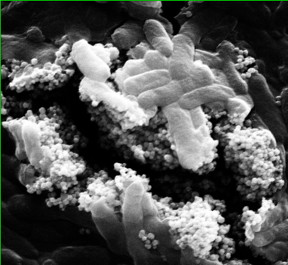 |
| Clusters of nanoparticles with phage viruses attached find and kill Escherichia coli bacteria in a lab test at Rice University. Researchers at Rice and the University of Science and Technology of China have developed a combination of antibacterial phages and magnetic nanoparticle clusters that infect and destroy bacteria that are usually protected by biofilms in water treatment systems. (Credit: Alvarez Group/Rice University) |
Abstract:
Magnetic nanoparticle clusters have the power to punch through biofilms to reach bacteria that can foul water treatment systems, according to scientists at Rice University and the University of Science and Technology of China.
Magnetized viruses attack harmful bacteria: Rice, China team uses phage-enhanced nanoparticles to kill bacteria that foul water treatment systems
Houston, TX | Posted on August 2nd, 2017The nanoclusters developed through Rice's Nanotechnology-Enabled Water Treatment (NEWT) Engineering Research Center carry bacteriophages – viruses that infect and propagate in bacteria – and deliver them to targets that generally resist chemical disinfection.
Without the pull of a magnetic host, these "phages" disperse in solution, largely fail to penetrate biofilms and allow bacteria to grow in solution and even corrode metal, a costly problem for water distribution systems.
The Rice lab of environmental engineer Pedro Alvarez and colleagues in China developed and tested clusters that immobilize the phages. A weak magnetic field draws them into biofilms to their targets.
The research is detailed in the Royal Society of Chemistry's Environmental Science: Nano.
"This novel approach, which arises from the convergence of nanotechnology and virology, has a great potential to treat difficult-to-eradicate biofilms in an effective manner that does not generate harmful disinfection byproducts," Alvarez said.
Biofilms can be beneficial in some wastewater treatment or industrial fermentation reactors owing to their enhanced reaction rates and resistance to exogenous stresses, said Rice graduate student and co-lead author Pingfeng Yu. "However, biofilms can be very harmful in water distribution and storage systems since they can shelter pathogenic microorganisms that pose significant public health concerns and may also contribute to corrosion and associated economic losses," he said.
The lab used phages that are polyvalent – able to attack more than one type of bacteria – to target lab-grown films that contained strains of Escherichia coli associated with infectious diseases and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which is prone to antibiotic resistance.
The phages were combined with nanoclusters of carbon, sulfur and iron oxide that were further modified with amino groups. The amino coating prompted the phages to bond with the clusters head-first, which left their infectious tails exposed and able to infect bacteria.
The researchers used a relatively weak magnetic field to push the nanoclusters into the film and disrupt it. Images showed they effectively killed E. coli and P. aeruginosa over around 90 percent of the film in a test 96-well plate versus less than 40 percent in a plate with phages alone.
The researchers noted bacteria may still develop resistance to phages, but the ability to quickly disrupt biofilms would make that more difficult. Alvarez said the lab is working on phage "cocktails" that would combine multiple types of phages and/or antibiotics with the particles to inhibit resistance.
Graduate student Ling-Li Li of the University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, is co-lead author of the paper. Co-authors are graduate student Sheng-Song Yu and Han-Qing Yu, a professor at the University of Science and Technology of China, and graduate student Xifan Wang and temporary research scientist Jacques Mathieu of Rice.
The National Science Foundation and its Rice-based NEWT Engineering Research Center supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,879 undergraduates and 2,861 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for happiest students and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to http://tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview .
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Nanotechnology-Enabled Water Treatment (NEWT):
Nanotechnology-Enabled Water Treatment (NEWT):
![]() George R. Brown School of Engineering
George R. Brown School of Engineering
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








