Home > Press > Electron partitioning process in graphene observed, a world first: Toward the realization of electron interferometer devices which utilize the wave nature of electrons
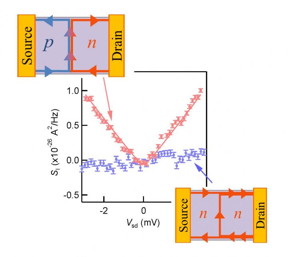 |
| This is the result of the shot noise measured in our device. Non-zero shot noise due to the electron partition process is observed in the p-n junction case (red dots). On the other hand, there appears no noise in the unipolar regime (blue dots). CREDIT: Osaka University |
Abstract:
Graphene, a single atomic layer of graphite with a carbon-layered structure, has been drawing much attention because of its abundant electronic properties and the possibilities of application due to its unique electronic structure. Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov extracted single-atom-thick crystallites from bulk graphite in 2004 for the first time. This results earned them the Nobel Prize in physics 2010.
Electron partitioning process in graphene observed, a world first: Toward the realization of electron interferometer devices which utilize the wave nature of electrons
Osaka, Japan | Posted on November 19th, 2015A group of researchers from Osaka University, the University of Tokyo, Kyoto University, and the National Institute for Materials Science precisely examined current-fluctuation ("shot noise") in the graphene p-n junction in the Quantum Hall (QH) regime and succeeded in observing electron partitioning taking place on the region along the p-n junction as current fluctuation. (See upper-left of Figure 1. Electron Partition Process.)
In addition, this group also clarified that electron partitioning did not take place under the absence of the p-n junction even in the QH regime.
It is expected that this group's achievement will lead to the clarification of the electron partition process in the graphene p-n junction in the QH regime because of its spin freedom and valley freedom and the realization of electron interference devices using the graphene p-n junction in the QH regime.
Kensuke Kobayashi (Professor, Graduate School of Science, Osaka University) and Sadashige Matsuo (Assistant Professor, Graduate School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo), in cooperation with research groups led by Teruo Ono (Professor, Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University) and Kazuhito Tsukagoshi (Research Fellow, International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics, National Institute for Materials Science), produced graphene samples capable of forming p-n junctions by combining gate electrodes and performed precise measurements of current-fluctuation ("shot noise") in the graphene p-n junction in the QH regime in the strong magnetic fields and at low temperatures.
As shown by Figure 1, this group clarified that while shot noise took place in the graphene p-n junction in the QH regime, shot noise did not take place in the absence of the graphene p-n junction. This group also verified that the quantity of the observed shot noise was nearly consistent with theoretical predictions.
These results directly demonstrated for the first time in the world that electron partitioning took place in the p-n junction in the QH regime, and microscopic characteristics of electron partitioning taking place in the graphene p-n junction were quantitatively established for the first time.
This research was published in the electronic version of Nature Communications (UK) on September 4, 2015. Furthermore, results closely related to this group's research results were simultaneously published in the Nature Communications by a joint group of researchers from Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation (NTT) and French research institutes. The latter research was performed totally independently from the former research, thus, it is noteworthy that the world's first research results were simultaneously announced from the two separate Japanese research teams.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Saori Obayashi
81-661-055-886
Copyright © Osaka University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








