Home > Press > Tiny carbon-capturing motors may help tackle rising carbon dioxide levels
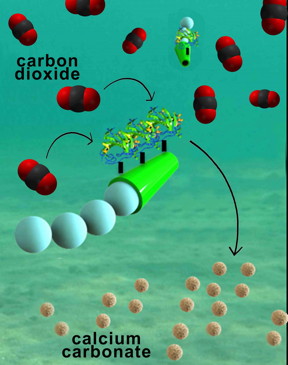 |
| Nanoengineers have invented tiny tube-shaped micromotors that zoom around in water and efficiently remove carbon dioxide. The surfaces of the micromotors are functionalized with the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which enables the motors to help rapidly convert carbon dioxide to calcium carbonate. CREDIT: Laboratory for Nanobioelectronics, UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering |
Abstract:
Machines that are much smaller than the width of a human hair could one day help clean up carbon dioxide pollution in the oceans. Nanoengineers at the University of California, San Diego have designed enzyme-functionalized micromotors that rapidly zoom around in water, remove carbon dioxide and convert it into a usable solid form.
Tiny carbon-capturing motors may help tackle rising carbon dioxide levels
San Diego, CA | Posted on September 24th, 2015The proof of concept study represents a promising route to mitigate the buildup of carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas in the environment, said researchers. The team, led by distinguished nanoengineering professor and chair Joseph Wang, published the work this month in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
"We're excited about the possibility of using these micromotors to combat ocean acidification and global warming," said Virendra V. Singh, a postdoctoral scientist in Wang's research group and a co-first author of this study.
In their experiments, nanoengineers demonstrated that the micromotors rapidly decarbonated water solutions that were saturated with carbon dioxide. Within five minutes, the micromotors removed 90 percent of the carbon dioxide from a solution of deionized water. The micromotors were just as effective in a sea water solution and removed 88 percent of the carbon dioxide in the same timeframe.
"In the future, we could potentially use these micromotors as part of a water treatment system, like a water decarbonation plant," said Kevin Kaufmann, an undergraduate researcher in Wang's lab and a co-author of the study.
The micromotors are essentially six-micrometer-long tubes that help rapidly convert carbon dioxide into calcium carbonate, a solid mineral found in eggshells, the shells of various marine organisms, calcium supplements and cement. The micromotors have an outer polymer surface that holds the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which speeds up the reaction between carbon dioxide and water to form bicarbonate. Calcium chloride, which is added to the water solutions, helps convert bicarbonate to calcium carbonate.
The fast and continuous motion of the micromotors in solution makes the micromotors extremely efficient at removing carbon dioxide from water, said researchers. The team explained that the micromotors' autonomous movement induces efficient solution mixing, leading to faster carbon dioxide conversion. To fuel the micromotors in water, researchers added hydrogen peroxide, which reacts with the inner platinum surface of the micromotors to generate a stream of oxygen gas bubbles that propel the micromotors around. When released in water solutions containing as little as two to four percent hydrogen peroxide, the micromotors reached speeds of more than 100 micrometers per second.
However, the use of hydrogen peroxide as the micromotor fuel is a drawback because it is an extra additive and requires the use of expensive platinum materials to build the micromotors. As a next step, researchers are planning to make carbon-capturing micromotors that can be propelled by water.
"If the micromotors can use the environment as fuel, they will be more scalable, environmentally friendly and less expensive," said Kaufmann.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liezel Labios
858-246-1124
Copyright © University of California - San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Marine/Watercraft
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
![]() Quantum tech in space? Scientists design remote monitoring system for inaccessible quantum devices February 11th, 2022
Quantum tech in space? Scientists design remote monitoring system for inaccessible quantum devices February 11th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








