Home > Press > Quantum tech in space? Scientists design remote monitoring system for inaccessible quantum devices
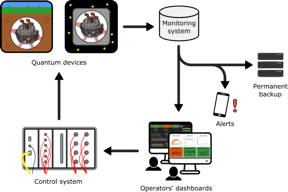 |
| Diagram detailing how the monitoring system works CREDIT University of Sussex |
Abstract:
Operating quantum technology in challenging environments, such as space, has moved a significant step forward after physicists working at the University of Sussex have developed a monitoring and control system blueprint for quantum devices and experiments.
Quantum tech in space? Scientists design remote monitoring system for inaccessible quantum devices
Brighton, UK | Posted on February 11th, 2022The system is presented in a peer reviewed paper published in Quantum Science and Technology. The paper details how the University’s Quantum Systems and Devices group has established remote access to monitor and control the environmental factors in their ultracold quantum laboratories.
The research has wider implications for operating quantum devices and carrying out experiments in inaccessible and unpredictable environments such as space, underground or those with unstable weather conditions, as well as for artificial intelligence (AI) and human collaboration and for online learning.
This could involve using quantum sensors in space to further our understanding of the fundamental laws of physics, in boats for GPS-free navigation, in electric vehicles to check the state of health of batteries or in hospitals for brain imaging.
Due to the high sensitivity of quantum apparatus, a stable environment is essential. The team has developed ways of keeping an eye on their experiments from afar by using remote monitoring technology to access information on factors such as temperature, pressure, laser beams and magnetic fields. Everyone in the team can see this information on dashboards so issues can be dealt with before they destabilise or disrupt experiments.
As the complexity of quantum technologies grows, the likelihood of breakdowns and severe delays increases. Environmental disturbances are usually only noticed when something goes wrong and then dealt with retrospectively. However, as the monitoring system allows the uninterrupted collection of environmental data, issues can be resolved in real-time.
The system builds upon previous work by the Quantum Systems and Devices group that allowed them to create a Bose-Einstein condensate in their university labs while working remotely from home.
Professor Peter Krüger, Principal Investigator in the group explains this latest development: “What our group have achieved here is a technical step towards automation, with less time spent debugging devices and the need to be onsite. Furthermore, this advancement has far-reaching implications that could pave the way to new smart technologies utilising AI/human collaboration.
“An algorithm can be written to source information from a mixture of human input, sensors and AI. As quantum technology become more complex, for example with more sophisticated sensors and quantum computers, these types of monitoring systems will become crucial. There are countless application possibilities. In the future you could find these systems monitoring quantum devices in places such as spacecraft, inside glaciers or closer to home in electric vehicles or hospitals.”
Dr Thomas Barrett, Research Fellow in the group and lead author of the paper says: “The system makes use of some technology that is already being used in many other sectors such as finance, farming and manufacturing and uniquely applies it to quantum devices.
“With this system, I could be cooking dinner at home and receive an emergency text message directly from my laboratory experiment saying there is a problem with the pressure in the vacuum chamber. In certain scenarios a quick remote fix could sort the problem giving me the freedom to continue with my evening. This could significantly speed up the pace at which we are able to achieve results by avoiding unnecessary maintenance visits to the labs and time spent working out what has gone wrong.”
“Whilst we have been able to exploit this system for controlling our experiments for homeworking, even more significantly, this technology provides a blueprint for monitoring the environment and carrying out research and operating technology in inaccessible, non-constant and unpredictable environments such as space, underground or below sea level. That’s where it gets really exciting and could provide far reaching impact.”
Dr Fedja Oručević , Lecturer in the group sees additional benefits to the development: “Having spent a lot of time in the last two years teaching students remotely, this development is hugely exciting. During lockdowns, lab-based courses were severely impacted with students unable to gain hands on experience in experimental physics. The consequences for teaching with a remote access system could reinvigorate the curriculum and open doors for lab-based teaching on online distance learning courses.”
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sam Keir
University of Sussex
Copyright © University of Sussex
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
Marine/Watercraft
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
![]() Expanding the freedom of design: powder coating on FRP thanks to conductive gelcoats with graphene nanotubes March 3rd, 2021
Expanding the freedom of design: powder coating on FRP thanks to conductive gelcoats with graphene nanotubes March 3rd, 2021
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








