Home > Press > High-performance 3-D microbattery suitable for large-scale on-chip integration
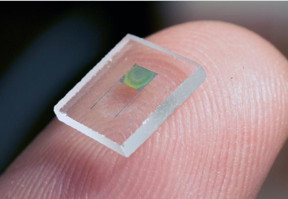 |
| This is an image of the holographically patterned microbattery. CREDIT: University of Illinois |
Abstract:
By combining 3D holographic lithography and 2D photolithography, researchers from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have demonstrated a high-performance 3D microbattery suitable for large-scale on-chip integration with microelectronic devices.
High-performance 3-D microbattery suitable for large-scale on-chip integration
Urbana, IL | Posted on May 12th, 2015"This 3D microbattery has exceptional performance and scalability, and we think it will be of importance for many applications," explained Paul Braun, a professor of materials science and engineering at Illinois. "Micro-scale devices typically utilize power supplied off-chip because of difficulties in miniaturizing energy storage technologies. A miniaturized high-energy and high-power on-chip battery would be highly desirable for applications including autonomous microscale actuators, distributed wireless sensors and transmitters, monitors, and portable and implantable medical devices."
"Due to the complexity of 3D electrodes, it is generally difficult to realize such batteries, let alone the possibility of on-chip integration and scaling. In this project, we developed an effective method to make high-performance 3D lithium-ion microbatteries using processes that are highly compatible with the fabrication of microelectronics," stated Hailong Ning, a graduate student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and first author of the article, "Holographic Patterning of High Performance on-chip 3D Lithium-ion Microbatteries," appearing in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"We utilized 3D holographic lithography to define the interior structure of electrodes and 2D photolithography to create the desired electrode shape." Ning added. "This work merges important concepts in fabrication, characterization, and modeling, showing that the energy and power of the microbattery are strongly related to the structural parameters of the electrodes such as size, shape, surface area, porosity, and tortuosity. A significant strength of this new method is that these parameters can be easily controlled during lithography steps, which offers unique flexibility for designing next-generation on-chip energy storage devices."
Enabled by a 3D holographic patterning technique--where multiple optical beams interfere inside the photoresist creating a desirable 3D structure--the battery possesses well-defined, periodically structured porous electrodes, that facilitates the fast transports of electrons and ions inside the battery, offering supercapacitor-like power.
"Although accurate control on the interfering optical beams is required to construct 3D holographic lithography, recent advances have significantly simplified the required optics, enabling creation of structures via a single incident beam and standard photoresist processing. This makes it highly scalable and compatible with microfabrication," stated John Rogers, a professor of materials science and engineering, who has worked with Braun and his team to develop the technology.
"Micro-engineered battery architectures, combined with high energy material such as tin, offer exciting new battery features including high energy capacity and good cycle lives, which provide the ability to power practical devices," stated William King, a professor of mechanical science and engineering, who is a co-author of this work.
###
The research is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering through the Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory at Illinois. In addition to Ning, Braun, Rogers, and King, study co-authors include graduate students, James H. Pikul, Runyu Zhang, Xuejiao Li, Sheng Xu, and Junjie Wang.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Paul V. Braun
217-244-7293
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Lab-on-a-chip
![]() Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
![]() Silicon-graphene hybrid plasmonic waveguide photodetectors beyond 1.55 μm March 13th, 2020
Silicon-graphene hybrid plasmonic waveguide photodetectors beyond 1.55 μm March 13th, 2020
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








