Home > Press > Piezoelectricity in a 2-D semiconductor: Berkeley Lab researchers discovery of piezoelectricty in molybdenum disulfide holds promise for future MEMS
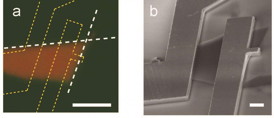 |
| To maximize piezoelectric coupling, electrodes (yellow dashed lines) were defined parallel to the zigzag edges (white dashed lines) of the MoS2 monolayer. Green and red colors denote the intensity of reflection and photoluminescence respectively. |
Abstract:
A door has been opened to low-power off/on switches in micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) and nanoelectronic devices, as well as ultrasensitive bio-sensors, with the first observation of piezoelectricity in a free standing two-dimensional semiconductor by a team of researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab).
Piezoelectricity in a 2-D semiconductor: Berkeley Lab researchers discovery of piezoelectricty in molybdenum disulfide holds promise for future MEMS
Berkeley, CA | Posted on December 22nd, 2014Xiang Zhang, director of Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division and an international authority on nanoscale engineering, led a study in which piezoelectricity - the conversion of mechanical energy into electricity or vice versa - was demonstrated in a free standing single layer of molybdenum disulfide, a 2D semiconductor that is a potential successor to silicon for faster electronic devices in the future.
"Piezoelectricity is a well-known effect in bulk crystals, but this is the first quantitative measurement of the piezoelectric effect in a single layer of molecules that has intrinsic in-plane dipoles," Zhang says. "The discovery of piezoelectricity at the molecular level not only is fundamentally interesting, but also could lead to tunable piezo-materials and devices for extremely small force generation and sensing."
Zhang, who holds the Ernest S. Kuh Endowed Chair at the University of California (UC) Berkeley and is a member of the Kavli Energy NanoSciences Institute at Berkeley, is the corresponding author of a paper in Nature Nanotechnology describing this research. The paper is titled "Observation of Piezoelectricity in Free-standing Monolayer MoS2." The co-lead authors are Hanyu Zhu and Yuan Wang, both members of Zhang's UC Berkeley research group. (See below for a complete list of co-authors.)
Since its discovery in 1880, the piezoelectric effect has found wide application in bulk materials, including actuators, sensors and energy harvesters. There is rising interest in using nanoscale piezoelectric materials to provide the lowest possible power consumption for on/off switches in MEMS and other types of electronic computing systems. However, when material thickness approaches a single molecular layer, the large surface energy can cause piezoelectric structures to be thermodynamically unstable.
Over the past couple of years, Zhang and his group have been carrying out detailed studies of molybdenum disulfide, a 2D semiconductor that features high electrical conductance comparable to that of graphene, but, unlike graphene, has natural energy band-gaps, which means its conductance can be switched off.
"Transition metal dichalcogenides such as molybdenum disulfide can retain their atomic structures down to the single layer limit without lattice reconstruction, even in ambient conditions," Zhang says. "Recent calculations predicted the existence of piezoelectricity in these 2D crystals due to their broken inversion symmetry. To test this, we combined a laterally applied electric field with nano-indentation in an atomic force microscope for the measurement of piezoelectrically-generated membrane stress."
Zhang and his group used a free-standing molybdenum disulfide single layer crystal to avoid any substrate effects, such as doping and parasitic charge, in their measurements of the intrinsic piezoelectricity. They recorded a piezoelectric coefficient of 2.9×10-10 C/m, which is comparable to many widely used materials such as zinc oxide and aluminum nitride.
"Knowing the piezoelectric coefficient is important for designing atomically thin devices and estimating their performance," says Nature paper co-lead author Zhu. "The piezoelectric coefficient we found in molybdenum disulfide is sufficient for use in low-power logic switches and biological sensors that are sensitive to molecular mass limits."
Zhang, Zhu and their co-authors also discovered that if several single layers of molybdenum disulfide crystal were stacked on top of one another, piezoelectricity was only present in the odd number of layers (1,3,5, etc.)
"This discovery is interesting from a physics perspective since no other material has shown similar layer-number sensitivity," Zhu says. "The phenomenon might also prove useful for applications in which we want devices consisting of as few as possible material types, where some areas of the device need to be non-piezoelectric."
In addition to logic switches and biological sensors, piezoelectricity in molybdenum disulfide crystals might also find use in the potential new route to quantum computing and ultrafast data-processing called "valleytronics." In valleytronics, information is encoded in the spin and momentum of an electron moving through a crystal lattice as a wave with energy peaks and valleys.
"Some types of valleytronic devices depend on absolute crystal orientation, and piezoelectric anisotropy can be employed to determine this,' says Nature paper co-lead author Wang. "We are also investigating the possibility of using piezoelectricity to directly control valleytronic properties such as circular dichroism in molybdenum disulfide."
###
In addition to Zhang, Zhu and Wang, other co-authors of the Nature paper were Jun Xiao, Ming Liu, Shaomin Xiong, Zi Jing Wong, Ziliang Ye, Yu Ye and Xiaobo Yin.
This research was supported by Light-Material Interactions in Energy Conversion, an Energy Frontier Research Center led by the California Institute of Technology, in which Berkeley Lab is a major partner. The Energy Frontier Research Center program is supported by DOE's Office of Science.
####
About DOE/Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world’s most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab’s scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. For more, visit www.lbl.gov.
The DOE Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lynn Yarris
510-486-5375
Xiang Zhang can be reached for comment at
(Office) (510-643-0638)
or (Mobile) (510-206-4792)
Copyright © DOE/Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() For more about the research of Xiang Zhang go here:
For more about the research of Xiang Zhang go here:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
NEMS
![]() IEDM - CEA-Leti Will Present 11 Papers and Host Workshop on Disruptive Technologies for Data Management November 7th, 2018
IEDM - CEA-Leti Will Present 11 Papers and Host Workshop on Disruptive Technologies for Data Management November 7th, 2018
![]() UT engineers develop first method for controlling nanomotors: Breakthrough for nanotechnology as UT engineers develop first method for switching the mechanical motion of nanomotors September 21st, 2018
UT engineers develop first method for controlling nanomotors: Breakthrough for nanotechnology as UT engineers develop first method for switching the mechanical motion of nanomotors September 21st, 2018
![]() Nano-kirigami: 'Paper-cut' provides model for 3D intelligent nanofabrication July 13th, 2018
Nano-kirigami: 'Paper-cut' provides model for 3D intelligent nanofabrication July 13th, 2018
![]() One string to rule them all April 17th, 2018
One string to rule them all April 17th, 2018
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
MEMS
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








