Home > Press > IBM Announces $3 Billion Research Initiative to Tackle Chip Grand Challenges for Cloud and Big Data Systems: Scientists and engineers to push limits of silicon technology to 7 nanometers and below and create post-silicon future
 |
| R&D investment to push limits of silicon to meet demands of cloud computing and big data systems courtesy: IBM |
Abstract:
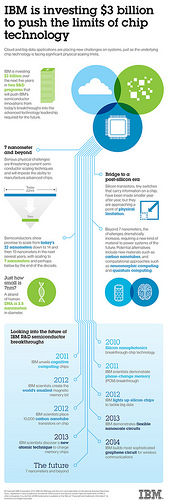
IBM (NYSE: IBM) today announced it is investing $3 billion over the next 5 years in two broad research and early stage development programs to push the limits of chip technology needed to meet the emerging demands of cloud computing and Big Data systems. These investments will push IBM's semiconductor innovations from today's breakthroughs into the advanced technology leadership required for the future.
IBM Announces $3 Billion Research Initiative to Tackle Chip Grand Challenges for Cloud and Big Data Systems: Scientists and engineers to push limits of silicon technology to 7 nanometers and below and create post-silicon future
Armonk, NY | Posted on July 10th, 2014The first research program is aimed at so-called "7 nanometer and beyond" silicon technology that will address serious physical challenges that are threatening current semiconductor scaling techniques and will impede the ability to manufacture such chips. The second is focused on developing alternative technologies for post-silicon era chips using entirely different approaches, which IBM scientists and other experts say are required because of the physical limitations of silicon based semiconductors.
Cloud and big data applications are placing new challenges on systems, just as the underlying chip technology is facing numerous significant physical scaling limits. Bandwidth to memory, high speed communication and device power consumption are becoming increasingly challenging and critical.
The teams will comprise IBM Research scientists and engineers from Albany and Yorktown, New York; Almaden, California; and Europe. In particular, IBM will be investing significantly in emerging areas of research that are already underway at IBM such as carbon nanoelectronics, silicon photonics, new memory technologies, and architectures that support quantum and cognitive computing.
These teams will focus on providing orders of magnitude improvement in system level performance and energy efficient computing. In addition, IBM will continue to invest in the nanosciences and quantum computing--two areas of fundamental science where IBM has remained a pioneer for over three decades.
7 nanometer technology and beyond
IBM Researchers and other semiconductor experts predict that while challenging, semiconductors show promise to scale from today's 22 nanometers down to 14 and then 10 nanometers in the next several years. However, scaling to 7 nanometers and perhaps below, by the end of the decade will require significant investment and innovation in semiconductor architectures as well as invention of new tools and techniques for manufacturing.
"The question is not if we will introduce 7 nanometer technology into manufacturing, but rather how, when, and at what cost?" said John Kelly, senior vice president, IBM Research. "IBM engineers and scientists, along with our partners, are well suited for this challenge and are already working on the materials science and device engineering required to meet the demands of the emerging system requirements for cloud, big data, and cognitive systems. This new investment will ensure that we produce the necessary innovations to meet these challenges."
"Scaling to 7nm and below is a terrific challenge, calling for deep physics competencies in processing nano materials affinities and characteristics. IBM is one of a very few companies who has repeatedly demonstrated this level of science and engineering expertise," said Richard Doherty, technology research director, The Envisioneering Group.
Bridge to a "Post-Silicon" Era
Silicon transistors, tiny switches that carry information on a chip, have been made smaller year after year, but they are approaching a point of physical limitation. Their increasingly small dimensions, now reaching the nanoscale, will prohibit any gains in performance due to the nature of silicon and the laws of physics. Within a few more generations, classical scaling and shrinkage will no longer yield the sizable benefits of lower power, lower cost and higher speed processors that the industry has become accustomed to.
With virtually all electronic equipment today built on complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, there is an urgent need for new materials and circuit architecture designs compatible with this engineering process as the technology industry nears physical scalability limits of the silicon transistor.
Beyond 7 nanometers, the challenges dramatically increase, requiring a new kind of material to power systems of the future, and new computing platforms to solve problems that are unsolvable or difficult to solve today. Potential alternatives include new materials such as carbon nanotubes, and non-traditional computational approaches such as neuromorphic computing, cognitive computing, machine learning techniques, and the science behind quantum computing.
As the leader in advanced schemes that point beyond traditional silicon-based computing, IBM holds over 500 patents for technologies that will drive advancements at 7nm and beyond silicon -- more than twice the nearest competitor. These continued investments will accelerate the invention and introduction into product development for IBM's highly differentiated computing systems for cloud, and big data analytics.
Several exploratory research breakthroughs that could lead to major advancements in delivering dramatically smaller, faster and more powerful computer chips, include quantum computing, neurosynaptic computing, silicon photonics, carbon nanotubes, III-V technologies, low power transistors and graphene:
Quantum Computing
The most basic piece of information that a typical computer understands is a bit. Much like a light that can be switched on or off, a bit can have only one of two values: "1" or "0." Described as superposition, this special property of qubits enables quantum computers to weed through millions of solutions all at once, while desktop PCs would have to consider them one at a time.
IBM is a world leader in superconducting qubit-based quantum computing science and is a pioneer in the field of experimental and theoretical quantum information, fields that are still in the category of fundamental science - but one that, in the long term, may allow the solution of problems that are today either impossible or impractical to solve using conventional machines. The team recently demonstrated the first experimental realization of parity check with three superconducting qubits, an essential building block for one type of quantum computer.
Neurosynaptic Computing
Bringing together nanoscience, neuroscience, and supercomputing, IBM and university partners have developed an end-to-end ecosystem including a novel non-von Neumann architecture, a new programming language, as well as applications. This novel technology allows for computing systems that emulate the brain's computing efficiency, size and power usage. IBM's long-term goal is to build a neurosynaptic system with ten billion neurons and a hundred trillion synapses, all while consuming only one kilowatt of power and occupying less than two liters of volume.
Silicon Photonics
IBM has been a pioneer in the area of CMOS integrated silicon photonics for over 12 years, a technology that integrates functions for optical communications on a silicon chip, and the IBM team has recently designed and fabricated the world's first monolithic silicon photonics based transceiver with wavelength division multiplexing. Such transceivers will use light to transmit data between different components in a computing system at high data rates, low cost, and in an energetically efficient manner.
Silicon nanophotonics takes advantage of pulses of light for communication rather than traditional copper wiring and provides a super highway for large volumes of data to move at rapid speeds between computer chips in servers, large datacenters, and supercomputers, thus alleviating the limitations of congested data traffic and high-cost traditional interconnects.
Businesses are entering a new era of computing that requires systems to process and analyze, in real-time, huge volumes of information known as Big Data. Silicon nanophotonics technology provides answers to Big Data challenges by seamlessly connecting various parts of large systems, whether few centimeters or few kilometers apart from each other, and move terabytes of data via pulses of light through optical fibers.
III-V technologies
IBM researchers have demonstrated the world's highest transconductance on a self-aligned III-V channel metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) field-effect transistors (FETs) device structure that is compatible with CMOS scaling. These materials and structural innovation are expected to pave path for technology scaling at 7nm and beyond. With more than an order of magnitude higher electron mobility than silicon, integrating III-V materials into CMOS enables higher performance at lower power density, allowing for an extension to power/performance scaling to meet the demands of cloud computing and big data systems.
Carbon Nanotubes
IBM Researchers are working in the area of carbon nanotube (CNT) electronics and exploring whether CNTs can replace silicon beyond the 7 nm node. As part of its activities for developing carbon nanotube based CMOS VLSI circuits, IBM recently demonstrated -- for the first time in the world -- 2-way CMOS NAND gates using 50 nm gate length carbon nanotube transistors.
IBM also has demonstrated the capability for purifying carbon nanotubes to 99.99 percent, the highest (verified) purities demonstrated to date, and transistors at 10 nm channel length that show no degradation due to scaling--this is unmatched by any other material system to date.
Carbon nanotubes are single atomic sheets of carbon rolled up into a tube. The carbon nanotubes form the core of a transistor device that will work in a fashion similar to the current silicon transistor, but will be better performing. They could be used to replace the transistors in chips that power data-crunching servers, high performing computers and ultra fast smart phones.
Carbon nanotube transistors can operate as excellent switches at molecular dimensions of less than ten nanometers - the equivalent to 10,000 times thinner than a strand of human hair and less than half the size of the leading silicon technology. Comprehensive modeling of the electronic circuits suggests that about a five to ten times improvement in performance compared to silicon circuits is possible.
Graphene
Graphene is pure carbon in the form of a one atomic layer thick sheet. It is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity, and it is also remarkably strong and flexible. Electrons can move in graphene about ten times faster than in commonly used semiconductor materials such as silicon and silicon germanium. Its characteristics offer the possibility to build faster switching transistors than are possible with conventional semiconductors, particularly for applications in the handheld wireless communications business where it will be a more efficient switch than those currently used.
Recently in 2013, IBM demonstrated the world's first graphene based integrated circuit receiver front end for wireless communications. The circuit consisted of a 2-stage amplifier and a down converter operating at 4.3 GHz.
Next Generation Low Power Transistors
In addition to new materials like CNTs, new architectures and innovative device concepts are required to boost future system performance. Power dissipation is a fundamental challenge for nanoelectronic circuits. To explain the challenge, consider a leaky water faucet -- even after closing the valve as far as possible water continues to drip -- this is similar to today's transistor, in that energy is constantly "leaking" or being lost or wasted in the off-state.
A potential alternative to today's power hungry silicon field effect transistors are so-called steep slope devices. They could operate at much lower voltage and thus dissipate significantly less power. IBM scientists are researching tunnel field effect transistors (TFETs). In this special type of transistors the quantum-mechanical effect of band-to-band tunneling is used to drive the current flow through the transistor. TFETs could achieve a 100-fold power reduction over complementary CMOS transistors, so integrating TFETs with CMOS technology could improve low-power integrated circuits.
Recently, IBM has developed a novel method to integrate III-V nanowires and heterostructures directly on standard silicon substrates and built the first ever InAs/Si tunnel diodes and TFETs using InAs as source and Si as channel with wrap-around gate as steep slope device for low power consumption applications.
"In the next ten years computing hardware systems will be fundamentally different as our scientists and engineers push the limits of semiconductor innovations to explore the post-silicon future," said Tom Rosamilia, senior vice president, IBM Systems and Technology Group. "IBM Research and Development teams are creating breakthrough innovations that will fuel the next era of computing systems."
IBM's historic contributions to silicon and semiconductor innovation include the invention and/or first implementation of: the single cell DRAM, the "Dennard scaling laws" underpinning "Moore's Law", chemically amplified photoresists, copper interconnect wiring, Silicon on Insulator, strained engineering, multi core microprocessors, immersion lithography, high speed silicon germanium (SiGe), High-k gate dielectrics, embedded DRAM, 3D chip stacking, and Air gap insulators.
IBM researchers also are credited with initiating the era of nano devices following the Nobel prize winning invention of the scanning tunneling microscope which enabled nano and atomic scale invention and innovation.
IBM will also continue to fund and collaborate with university researchers to explore and develop the future technologies for the semiconductor industry. In particular, IBM will continue to support and fund university research through private-public partnerships such as the NanoElectornics Research Initiative (NRI), and the Semiconductor Advanced Research Network (STARnet), and the Global Research Consortium (GRC) of the Semiconductor Research Corporation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Steve Tomasco
IBM Media Relations
917-687-4588
Ari Entin
IBM Media Relations
408-927-2272
Copyright © IBM
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Brain-Computer Interfaces
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
![]() New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








