Home > Press > ‘White graphene’ halts rust in high temps: Rice U. researchers find nano-thin films of hexagonal boron nitride protect materials from oxidizing
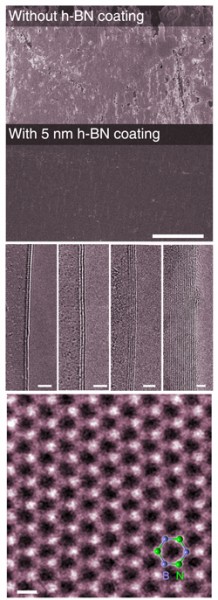 |
| Rice University researchers have discovered that sheets of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) as little as one atom thick can protect metals in harsh environments at up to 1,100 degrees Celsius. The top image shows uncoated nickel oxidized after exposure to high temperature in an oxygen-rich environment. The second shows nickel exposed to the same conditions with a 5-nanometer coat of h-BN. The third shows electron microscope images of two, three, four and many-layer h-BN films. The bottom image of an h-BN sheet shows the hexagonal arrangement of nitrogen (bright) and boron atoms. Images by Zheng Liu |
Abstract:
Atomically thin sheets of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) have the handy benefit of protecting what's underneath from oxidizing even at very high temperatures, Rice University researchers have discovered.
‘White graphene’ halts rust in high temps: Rice U. researchers find nano-thin films of hexagonal boron nitride protect materials from oxidizing
Houston, TX | Posted on October 6th, 2013One or several layers of the material sometimes called "white graphene" keep materials from oxidizing - or rusting — up to 1,100 degrees Celsius (2,012 degrees Fahrenheit), and can be made large enough for industrial applications, they said.
The Rice study led by materials scientists Pulickel Ajayan and Jun Lou appears in the online journal Nature Communications.
Oxidation prevention is already big business, but no products available now work on the scale of what the Rice lab is proposing. The researchers see potential for very large sheets of h-BN only a few atoms thick made by scalable vapor deposition methods.
"We think this opens up new opportunities for two-dimensional material," said Lou, an associate professor of mechanical engineering and materials science. "Everybody has been talking about these materials for electronic or photonic devices, but if this can be realized on a large scale, it's going to cover a broad spectrum of applications."
Lou said ultrathin h-BN protection might find a place in turbines, jet engines, oil exploration or underwater or other harsh environments where minimal size and weight would be an advantage, though wear and abrasion could become an issue and optimum thicknesses need to be worked out for specific applications.
It's effectively invisible as well, which may make it useful for protecting solar cells from the elements, he said. "Essentially, this can be a very useful structural material coating," Lou said.
The researchers made small sheets of h-BN via chemical vapor deposition (CVD), a process they said should be scalable for industrial production. They first grew the thin material on nickel foil and found it withstood high temperature in an oxygen-rich environment. They also grew h-BN on graphene and found they could transfer sheets of h-BN to copper and steel with similar results.
"What's amazing is that these layers are ultrathin and they stand up to such ultrahigh temperatures," Ajayan said. "At a few nanometers wide, they're a totally non-invasive coating. They take almost no space at all."
Lead authors are Rice postdoctoral researcher Zheng Liu and graduate student Yongji Gong. Co-authors are Rice graduate student Lulu Ma and Senior Faculty Fellow Robert Vajtai; Wu Zhou, a Wigner Fellow, and Juan Carlos Idrobo, a staff scientist at Oak Ridge National Laboratory; Jingjiang Yu of Agilent Technologies; Jeil Jung, a research fellow at the National University of Singapore and a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Texas at Austin; and Allan MacDonald, the Sid W. Richardson Foundation Regents Chair Professor at the University of Texas at Austin. Ajayan is the Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science and of chemistry at Rice.
The Army Research Office, the Office of Naval Research, the Welch Foundation, the Korean Institute of Machinery and Materials, the National Science Foundation, Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the Department of Energy supported the research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mike Williams
senior media relations specialist
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Aerospace/Space
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
![]() The National Space Society Congratulates SpaceX on Starship’s 7th Test Flight: Latest Test of the Megarocket Hoped to Demonstrate a Number of New Technologies and Systems January 17th, 2025
The National Space Society Congratulates SpaceX on Starship’s 7th Test Flight: Latest Test of the Megarocket Hoped to Demonstrate a Number of New Technologies and Systems January 17th, 2025
Industrial
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








