Home > Press > Hybrid ribbons a gift for powerful batteries: Rice lab finds vanadium oxide/graphene material works well for lithium-ion storage
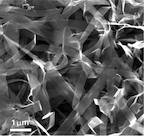 |
| Graphene-coated ribbons of vanadium oxide, seen in a scanning electron microscope image, might be the best electrode for lithium-ion batteries yet tested, according to researchers at Rice University. Credit: Ajayan Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
Hybrid ribbons of vanadium oxide (VO2) and graphene may accelerate the development of high-power lithium-ion batteries suitable for electric cars and other demanding applications.
Hybrid ribbons a gift for powerful batteries: Rice lab finds vanadium oxide/graphene material works well for lithium-ion storage
Houston, TX | Posted on March 25th, 2013The Rice University lab of materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan determined that the well-studied material is a superior cathode for batteries that could supply both high energy density and significant power density. The research appears online this month in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters.
The ribbons created at Rice are thousands of times thinner than a sheet of paper, yet have potential that far outweighs current materials for their ability to charge and discharge very quickly. Cathodes built into half-cells for testing at Rice fully charged and discharged in 20 seconds and retained more than 90 percent of their initial capacity after more than 1,000 cycles.
"This is the direction battery research is going, not only for something with high energy density but also high power density," Ajayan said. "It's somewhere between a battery and a supercapacitor."
The ribbons also have the advantage of using relatively abundant and cheap materials. "This is done through a very simple hydrothermal process, and I think it would be easily scalable to large quantities," he said.
Ajayan said vanadium oxide has long been considered a material with great potential, and in fact vanadium pentoxide has been used in lithium-ion batteries for its special structure and high capacity. But oxides are slow to charge and discharge, due to their low electrical conductivity. The high-conductivity graphene lattice that is literally baked in solves that problem nicely, he said, by serving as a speedy conduit for electrons and channels for ions.
The atom-thin graphene sheets bound to the crystals take up very little bulk. In the best samples made at Rice, fully 84 percent of the cathode's weight was the lithium-slurping VO2, which held 204 milliamp hours of energy per gram. The researchers, led by Rice graduate student Yongji Gong and lead author Shubin Yang, said they believe that to be among the best overall performance ever seen for lithium-ion battery electrodes.
"One challenge to production was controlling the conditions for the co-synthesis of VO2 ribbons with graphene," Yang said. The process involved suspending graphene oxide nanosheets with powdered vanadium pentoxide (layered vanadium oxide, with two atoms of vanadium and five of oxygen) in water and heating it in an autoclave for hours. The vanadium pentoxide was completely reduced to VO2, which crystallized into ribbons, while the graphene oxide was reduced to graphene, Yang said. The ribbons, with a web-like coating of graphene, were only about 10 nanometers thick, up to 600 nanometers wide and tens of micrometers in length.
"These ribbons were the building blocks of the three-dimensional architecture," Yang said. "This unique structure was favorable for the ultrafast diffusion of both lithium ions and electrons during charge and discharge processes. It was the key to the achievement of excellent electrochemical performance."
In testing the new material, Yang and Gong found its capacity for lithium storage remained stable after 200 cycles even at high temperatures (167 degrees Fahrenheit) at which other cathodes commonly decay, even at low charge-discharge rates.
"We think this is real progress in the development of cathode materials for high-power lithium-ion batteries," Ajayan said, suggesting the ribbons' ability to be dispersed in a solvent might make them suitable as a component in the paintable batteries developed in his lab.
Co-authors of the new paper are Rice graduate students Daniel Hashim and Lulu Ma; research scientist Zheng Liu; former Rice visiting researcher Liang Zhan, now an associate professor at East China University of Science and Technology in Shanghai; and faculty fellow Robert Vajtai. Ajayan is the Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Engineering and a professor of mechanical engineering and materials science, chemistry, and chemical and biomolecular engineering.
The work was funded by the U.S. Army Research Office and the Office of Naval Research through a Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative grant and a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship grant.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,708 undergraduates and 2,374 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to tinyurl.com/AboutRiceU.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








