Home > Press > Researchers Devise New Means For Creating Elastic Conductors
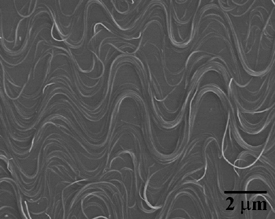 |
| The buckled nanotubes look like squiggly lines on a flat surface. |
Abstract:
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new method for creating elastic conductors made of carbon nanotubes, which will contribute to large-scale production of the material for use in a new generation of elastic electronic devices.
Researchers Devise New Means For Creating Elastic Conductors
Raleigh, NC | Posted on January 24th, 2012"We're optimistic that this new approach could lead to large-scale production of stretchable conductors, which would then expedite research and development of elastic electronic devices," says Dr. Yong Zhu, an assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at NC State, and lead author of a paper describing the new technique.
Stretchable electronic devices would be both more resilient and able to conform to various shapes. Potential applications include devices that can be incorporated into clothing, implantable medical devices, and sensors that can be stretched over unmanned aerial vehicles.
To develop these stretchable electronics, one needs to create conductors that are elastic and will reliably transmit electric signals regardless of whether they are being stretched.
One way of making conductive materials more elastic is to "buckle" them. Zhu's new method buckles carbon nanotubes on the plane of the substrate. Think of the nanotubes as forming squiggly lines on a piece of paper, rather than an accordion shape that zigs up and down with only the bottom parts touching the sheet of paper. Zhu's team used carbon nanotubes because they are sturdy, stable, excellent conductors and can be aligned into ribbons.
The new process begins by placing aligned carbon nanotubes on an elastic substrate using a transfer printing process. The substrate is then stretched, which separates the nanotubes while maintaining their parallel alignment.
Strikingly, when the substrate is relaxed, the nanotubes do not return to their original positions. Instead, the nanotubes buckle - creating what looks like a collection of parallel squiggly lines on a flat surface.
The carbon nanotubes are now elastic - they can be stretched - but they have retained their electrical properties.
The key benefit of this new method is that it will make manufacturing of elastic conductors significantly more efficient, because the carbon nanotubes can be applied before the substrate is stretched. This is compatible with existing manufacturing processes. "For example, roll-to-roll printing techniques could be adapted to take advantage of our new method," Zhu says.
A paper describing the new approach, "Buckling of Aligned Carbon Nanotubes as Stretchable Conductors: A New Manufacturing Strategy," was published online Jan. 23 in Advanced Materials. The paper was co-authored by Feng Xu, a Ph.D. student at NC State. The research was funded by the National Science Foundation.
In another new paper, Zhu's team has demonstrated for the first time that carbon nanotubes can be buckled using a technique in which the elastic substrate is stretched before the nanotubes are applied. The substrate is then relaxed, forcing the nanotubes to buckle out of plane. The nanotubes form a ribbon that curves up and down like the bellows of an accordion. This second technique has been used before with other materials. This second paper, "Wavy Ribbons of Carbon Nanotubes for Stretchable Conductors," was published Jan. 19 in Advanced Functional Materials.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
News Services
919.515.6386
Dr. Yong Zhu
919.513.7735
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Download -“Wavy Ribbons of Carbon Nanotubes for Stretchable Conductors.”
Download -“Wavy Ribbons of Carbon Nanotubes for Stretchable Conductors.”
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
![]() Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Textiles/Clothing
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
![]() Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








