Home > Press > NSF Announces Results of the Materials Research Centers and Teams Competition: The centers and teams support outstanding interdisciplinary materials research and education
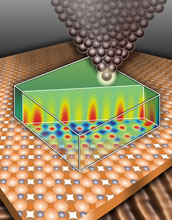 |
| This image shows an artistic rendering of the metal tip of the special microscope used to perform 3D force field mapping of materials at Yale University. The microscope is a unique combined scanning tunneling/atomic force microscope that can operate at temperatures close to absolute zero. It can simultaneously map out the chemical and electrical properties of surfaces at the atomic scale, while also describing the precise layout and identity of the atoms that make up the surface of the material.
Credit: Udo Schwarz, Yale University |
Abstract:
The National Science Foundation (NSF) today announced awards for three Materials Interdisciplinary Research Teams (MIRT) and nine Centers of Excellence in Materials Research and Innovation, also known as Materials Research Science and Engineering Centers (MRSEC). The awards resulted from the 2011 Materials Research Centers and Teams competition (solicitation NSF 10-568).
NSF Announces Results of the Materials Research Centers and Teams Competition: The centers and teams support outstanding interdisciplinary materials research and education
Arlington, VA | Posted on September 10th, 2011The centers and teams support outstanding multi- and inter-disciplinary materials research and education addressing fundamental problems in science and engineering and foster active collaboration among universities, international collaborators, industry and national laboratories.
"In light of the strong interest on the part of the administration in materials research through the recently announced Materials Genome Initiative, these awards are timely in order to advance new discoveries, support a strong workforce and strengthen infrastructure" said Janice Hicks, deputy director for NSF's Division of Materials Research. "These multidisciplinary awards will especially promote areas such as next-generation electronics and photonics and bio- and soft-materials. The centers will provide leadership for the country pertaining to new materials and new materials phenomena that could ultimately address national needs including sustainability and innovation. We are especially excited about the collaborations internationally and with industry that will give the students and postdocs in the centers experiences valuable to their lives as scientists and engineers."
Three new MIRTs were created as a result of the competition:
The Columbia University MIRT, Building Functional Nanoarchitectures in van der Waals Materials examines the assembly and physical properties of new composite materials created by 'nano-laminating' atomic sheets of different van der Waals materials which have novel electronic properties and are expected to lead to new nanoelectronic devices. The team seeks to exploit a wide range of new material building blocks, including both inorganic and organic materials. The research will focus on understanding the physical principles governing assembly of such materials and examine their distinctive optical, thermal and mechanical properties.
The University of Texas at Austin MIRT, Exploring Unusual Properties of Transition Metal Oxides will synthesize new transition metal oxides and develop a fundamental understanding of correlated electron behavior in these materials, which produce such intriguing properties as high temperature superconductivity, Mott insulator transitions and the newly discovered topological insulator state of matter. The work is anticipated to impact new materials development for the next generation of electronic and electrochemical energy devices.
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill MIRT, Stressed Polymers - Exploiting Tension in Soft Matter will develop new principles in soft materials design where mechanical stress in materials is generated, managed, and harvested by molecular engineering. The research may lead to novel multifunctional polymer particles and substrates that autonomously change their shape, surface structure, mechanical and optical properties. These novel materials have potential applications in, among other areas, cancer therapy, imaging and medical diagnosis.
Nine MRSECs were funded in 2011
The three new centers created as a result of the competition are:
The University of Utah Center, Next-Generation Materials for Plasmonics and Spintronics will foster interdisciplinary basic research on new materials in two Interdisciplinary Research Groups (IRGs) entitled "Plasmonic Metamaterials from the Terahertz to the Ultraviolet" and "Organic Spintronics." IRG-1 focuses on exploiting the properties of artificially structured materials (metamaterials) across a broad range of the electromagnetic spectrum. IRG-2 will advance our understanding of the role of spin interactions in organic materials for the development of a range of different spin-related organic devices. Applications range from telecommunications and imaging to new magnetic memory and low-cost organic photovoltaic cells.
The Research Triangle Center, Programmable Assembly of Soft Matter will focus on the study and development of soft matter components to be used in programmable assembly and functional and hybrid materials. IRG-1 will develop a fundamental understanding of self-assembly of materials from colloids, while IRG-2 will establish the rules for the design of "syntactomers," molecules that consist of a defined, repeated sequence of "letters" like amino acids. These projects will impact the production of hybrid photonic and phononic crystals, self-healing materials, "smart" gels, drug delivery materials, tissue implants and 3-D cell culture.
The University of Michigan Center, Photonic and Multiscale Nanomaterials has two IRGs that will develop novel multiscale materials for nanophotonics. IRG-1 will focus on wide bandgap nanostructured materials for high-efficiency visible light emitters, lasers, energy conversion and novel quantum devices. IRG-2 will focus on metamaterials for potential applications in communication, sensing and sub-wavelength imaging.
Six awards will support established centers which have successfully recompeted, in most cases with a significantly different focus of materials research and education:
The Materials Research Laboratory at the University of California at Santa Barbara addresses fundamental problems in materials science and engineering through three IRGs including: IRG-1 on self-assembling materials for new adhesives and materials for hostile biological and underwater environments; IRG-2 on the unique properties of complex oxides, along with new strategies for materials that will significantly advance energy and environmental applications; and IRG-3 on the science and engineering of two-phase nanoscopic materials with unprecedented magnetic, radiation-resistance and thermal transport properties.
The Cornell Center for Materials Research will pursue a vigorous research program through 3 IRGs: IRG-1 focuses on fundamental research and control of complex electronic materials that have spectacular electronic and magnetic properties, including high temperature superconductivity; IRG-2 on understanding and applying new mechanisms to manipulate electron spins in both ferromagnetic and non-ferromagnetic materials, which could potentially enable nonvolatile magnetic memory technologies that are much smaller, more energy efficient, more reliable, faster and less expensive than competing strategies; and IRG-3, which explores atomic membranes an exciting new class of two-dimensional, free-standing materials only one atom thick yet mechanically robust, chemically stable and virtually impermeable.
The theme of the Northwestern University Center is Multifunctional Nanoscale Materials Structures. The goals of the center consist of understanding the fundamental principles and behaviors of complex nanomaterials systems, transferring research results into new technologies and industries and initiating collaborations with national and international partners. Researchers are organized into three IRGs: IRG-1 on controlling fluxes of charge and energy at hybrid interfaces; IRG-2 on the fundamentals of amorphous oxide semiconductors; and IRG-3 on plasmonically-encoded materials for amplified sensing and information manipulation.
The Laboratory for Research on the Structure of Matter at the University of Pennsylvania supports four IRGs. The first IRG explores the interplay of curvature- and elasticity-induced interactions in liquid crystals, colloids and on interfaces. IRG-2 creates materials inspired by virology from novel synthetic macromolecules such as self-assembled Janus dendrimers and designer proteins to be used for sensing, communication and actuation. IRG-3 investigates disordered packings of atoms, colloids and grains to understand how localized rearrangements of constituents organize under load. The concepts generated will provide new strategies for predicting whether materials will fail, and for synthesis of tough materials. IRG-4 builds novel inter-dimensional materials from nanocrystal particles and measures their emergent electronic, optical, acoustic and magnetic properties.
The University of Wisconsin-Madison Center on Structured Interfaces unites a wide array of researchers all focused on the central theme of "Structured Interfaces" and is organized into three IRGs: IRG-1 focuses on new multi-element compounds and semiconductor materials, IRG-2 on charge transport near and across interfaces between organic and inorganic materials and IRG-3 on the synthesis and processes of new classes of functional liquid crystalline materials, composites and interfaces. Industries from displays to solar cells, to electronics and biomedical sensors could benefit from the results produced by these three interdisciplinary research groups.
The Center for Research on Interface Structure and Phenomena at Yale University brings together researchers to discover and develop novel materials engineered at the atomic scale. IRG-1 will investigate novel chemical, electronic and magnetic properties that arise from complex oxide interfaces. IRG-2 will develop new bulk metallic glasses and advance the fundamental understanding of their behavior, enabling surface property engineering. These IRGs will advance a wide range of technologies spanning from computation, communication, energy and medical applications.
####
About National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent federal agency that supports fundamental research and education across all fields of science and engineering. In fiscal year (FY) 2011, its budget is about $6.9 billion. NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to nearly 2,000 universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives over 45,000 competitive requests for funding, and makes over 11,500 new funding awards. NSF also awards over $400 million in professional and service contracts yearly.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contacts
Lisa Van Pay
NSF
(703) 292-8796
Program Contacts
Mary E. Galvin
NSF
(703) 292-8562
Sean L. Jones
NSF
(703) 292-2986
Thomas P. Rieker
NSF
(703) 292-4914
Z. Charles Ying
NSF
(703) 292-8428
Copyright © National Science Foundation
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








