Home > Press > Stretching Old Material Yields New Results for Energy- and Environment-related Devices
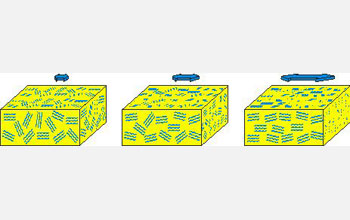 |
| This image illustrates how the channels in a polymer electrolyte membrane material change when you stretch it. On the left is an unstretched sample of the material. The middle sample has been stretched at a ratio of 2:1, while the sample on the right, which shows the most channel alignment, has been stretched at a ratio of 4:1.
Credit: Dr. Jing Li and Prof. Louis Madsen of Virginia Tech |
Abstract:
Researchers at Virginia Tech in Blacksburg, Va. recently found a way to improve electricity generating fuel cells, potentially making them more efficient, powerful and less expensive. Specifically, they discovered a way to speed up the flow and filtering of water or ions, which are necessary for fuel cells to operate.
Stretching Old Material Yields New Results for Energy- and Environment-related Devices
Arlington, VA | Posted on June 21st, 2011Simply put, the researchers stretched Nafion, a polymer electrolyte membrane, or PEM, commonly used in fuel cells and increased the speed at which it selectively filters substances from ions and water.
The resulting process could be important to a number of energy and environment-related applications such as any of several industrial processes that involve filtering, including improving batteries in cars, water desalination and even the production of artificial muscles for robots.
The journal Nature Materials published the results in its June 19 issue in the article, "Linear coupling of alignment with transport in a polymer electrolyte membrane," by Jing Li, Jong Keun Park, Robert B. Moore and Louis A. Madsen, all with the chemistry department in the College of Science and the Macromolecules and Interfaces Institute at Virginia Tech.
"I got the idea for some of these experiments after I saw Bob Moore give a talk at the University of North Carolina about Nafion when I was a post-doc there working with liquid crystals," said Madsen, an assistant professor of physical, polymer and materials chemistry who led the study.
In order to improve PEMs, Madsen and Virginia Tech Chemistry Professor Robert Moore studied exactly how water moves through Nafion at the molecular level and measured how changes in the structure of the material affected water flow. They found stretching it caused channels in the PEM material to align in the direction of the stretch, allowing water to flow through faster.
"Stretching drastically influences the degree of alignment," said Madsen. "So the molecules move faster along the direction of the stretch, and in a very predictable way. These materials actually share some properties with liquid crystals--molecules that line up with each other and are used in every LCD television, projector and screen."
"This is a very clever approach which demonstrates the advantages of interdisciplinary materials research and which may offer important benefits to both energy technologies and sustainability of our natural resources," said Andy Lovinger, polymers program director in the National Science Foundation's Division of Materials Research, which funded the study.
Nafion was discovered in the 1960's and is made up of molecules that combine the non-stick and tough nature of Teflon with the conductive properties of an acid. It is one of many PEMs used to filter water and ions that the researchers say could benefit from the stretching process.
####
About National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent federal agency that supports fundamental research and education across all fields of science and engineering. In fiscal year (FY) 2010, its budget is about $6.9 billion. NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to nearly 2,000 universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives over 45,000 competitive requests for funding, and makes over 11,500 new funding awards. NSF also awards over $400 million in professional and service contracts yearly.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contacts
Lisa Van Pay
NSF
(703) 292-8796
Susan Trulove
Virginia Tech
(540) 231-5646
Program Contacts
Andrew J. Lovinger
NSF
(703) 292-4933
Principal Investigators
Louis Madsen
Virginia Tech
(540) 231-1270
Copyright © National Science Foundation
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








