Home > Press > “Nanoscoops” Could Spark a New Generation of Electric Automobile Batteries
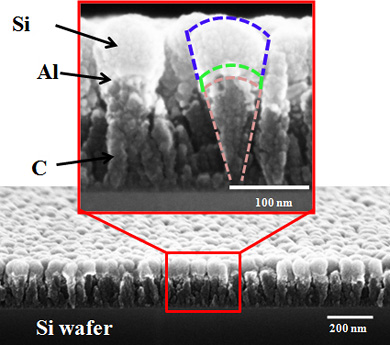 |
| Researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute developed an entirely new type of nanomaterial that could enable the next generation of high-power rechargeable lithium (Li)-ion batteries for electric automobiles, laptop computers, mobile phones, and other devices. The material, called a “nanoscoop” because it resembles a cone with a scoop of ice cream on top, is shown in the above scanning electron microscope image. Nanoscoops can withstand extremely high rates of charge and discharge that would cause today’s Li-ion batteries to rapidly deteriorate and fail. |
Abstract:
New nanoengineered batteries developed at Rensselaer exhibit remarkable power density, charging more than 40 times faster than today's lithium-ion batteries
“Nanoscoops” Could Spark a New Generation of Electric Automobile Batteries
Troy, NY | Posted on January 4th, 2011An entirely new type of nanomaterial developed at Rensselaer could enable the next generation of high-power rechargeable lithium (Li)-ion batteries for electric automobiles, as well as batteries for laptop computers, mobile phones, and other portable devices.
The new material, dubbed a "nanoscoop" because its shape resembles a cone with a scoop of ice cream on top, can withstand extremely high rates of charge and discharge that would cause conventional electrodes used in today's Li-ion batteries to rapidly deteriorate and fail. The nanoscoop's success lies in its unique material composition, structure, and size.
The Rensselaer research team, led by Professor Nikhil Koratkar, demonstrated how a nanoscoop electrode could be charged and discharged at a rate 40 to 60 times faster than conventional battery anodes, while maintaining a comparable energy density. This stellar performance, which was achieved over 100 continuous charge/discharge cycles, has the team confident that their new technology holds significant potential for the design and realization of high-power, high-capacity Li-ion rechargeable batteries.
"Charging my laptop or cell phone in a few minutes, rather than an hour, sounds pretty good to me," said Koratkar, a professor in the Department of Mechanical, Aerospace, and Nuclear Engineering at Rensselaer. "By using our nanoscoops as the anode architecture for Li-ion rechargeable batteries, this is a very real prospect. Moreover, this technology could potentially be ramped up to suit the demanding needs of batteries for electric automobiles."
Batteries for all-electric vehicles must deliver high power densities in addition to high energy densities, Koatkar said. These vehicles today use supercapacitors to perform power-intensive functions, such as starting the vehicle and rapid acceleration, in conjunction with conventional batteries that deliver high energy density for normal cruise driving and other operations. Koratkar said the invention of nanoscoops may enable these two separate systems to be combined into a single, more efficient battery unit.
Results of the study were detailed in the paper "Functionally Strain-Graded Nanoscoops for High Power Li-Ion Battery Anodes," published Thursday by the journal Nano Letters. See the full paper at: pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nl102981d
The anode structure of a Li-ion battery physically grows and shrinks as the battery charges or discharges. When charging, the addition of Li ions increases the volume of the anode, while discharging has the opposite effect. These volume changes result in a buildup of stress in the anode. Too great a stress that builds up too quickly, as in the case of a battery charging or discharging at high speeds, can cause the battery to fail prematurely. This is why most batteries in today's portable electronic devices like cell phones and laptops charge very slowly - the slow charge rate is intentional and designed to protect the battery from stress-induced damage.
The Rensselaer team's nanoscoop, however, was engineered to withstand this buildup of stress. Made from a carbon (C) nanorod base topped with a thin layer of nanoscale aluminum (Al) and a "scoop" of nanoscale silicon (Si), the structures are flexible and able to quickly accept and discharge Li ions at extremely fast rates without sustaining significant damage. The segmented structure of the nanoscoop allows the strain to be gradually transferred from the C base to the Al layer, and finally to the Si scoop. This natural strain gradation provides for a less abrupt transition in stress across the material interfaces, leading to improved structural integrity of the electrode.
The nanoscale size of the scoop is also vital since nanostructures are less prone to cracking than bulk materials, according to Koratkar.
"Due to their nanoscale size, our nanoscoops can soak and release Li at high rates far more effectively than the macroscale anodes used in today's Li-ion batteries," he said. "This means our nanoscoop may be the solution to a critical problem facing auto companies and other battery manufacturers - how can you increase the power density of a battery while still keeping the energy density high?"
A limitation of the nanoscoop architecture is the relatively low total mass of the electrode, Koratkar said. To solve this, the team's next steps are to try growing longer scoops with greater mass, or develop a method for stacking layers of nanoscoops on top of each other. Another possibility the team is exploring includes growing the nanoscoops on large flexible substrates that can be rolled or shaped to fit along the contours or chassis of the automobile.
Along with Koratkar, authors on the paper are Toh-Ming Lu, the R.P. Baker Distinguished Professor of Physics and associate director of the Center for Integrated Electronics at Rensselaer; and Rahul Krishnan, a graduate student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Rensselaer.
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Mullaney
Phone: (518) 276-6161
Copyright © Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








