Home > Press > TU scientists in Nature: Better control of building blocks for quantum computer
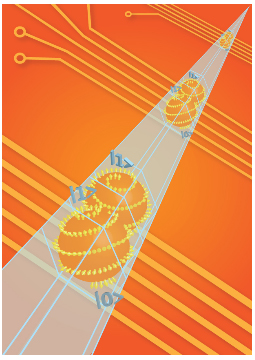 |
| Nanowire-1-WEB: Artist's impression of nanowire qubits. Credit: Gemma Plum |
Abstract:
Scientists from the Kavli Institute of Nanoscience at Delft University of Technology and Eindhoven University of Technology have succeeded in controlling the building blocks of a future super-fast quantum computer.
TU scientists in Nature: Better control of building blocks for quantum computer
The Netherlands | Posted on December 23rd, 2010They are now able to manipulate these building blocks (qubits) with electrical rather than magnetic fields, as has been the common practice up till now. They have also been able to embed these qubits into semiconductor nanowires. The scientists' findings have been published in the current issue of the science journal Nature (23 December).
Spin
A qubit is the building block of a possible, future quantum computer, which would far outstrip current computers in terms of speed. One way to make a qubit is to trap a single electron in semiconductor material. A qubit can, just like a normal computer bit, adopt the states '0' and '1'. This is achieved by using the spin of an electron, which is generated by spinning the electron on its axis. The electron can spin in two directions (representing the '0' state and the '1' state).
Electrical instead of magnetic
Until now, the spin of an electron has been controlled by magnetic fields. However, these field are extremely difficult to generate on a chip. The electron spin in the qubits that are currently being generated by the Dutch scientists can be controlled by a charge or an electric field, rather than by magnetic fields. This form of control has major advantages, as Leo Kouwenhoven, scientist at the Kavli Institute of Nanoscience at TU Delft, points out: "These spin-orbit qubits combine the best of both worlds. They employ the advantages of both electronic control and information storage in the electron spin."
Nanowires
There is another important new development in the Dutch research: the scientists have been able to embed the qubits (two) into nanowires made of a semiconductor material (indium arsenide). These wires are of the order of nanometres in diameter and micrometres in length. Kouwenhoven: "These nanowires are being increasingly used as convenient building blocks in nanoelectronics. Nanowires are an excellent platform for quantum information processing, among other applications."
Reference:
Nadj-Perge, S, S.M. Frolov, E.P.A.M. Bakkers and L.P. Kouwenhoven (2010) Spin-Orbit qubit in a semiconductor nanowire. Nature 468, 1084 - 1087.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Leo Kouwenhoven, full professor Quantum Transport, Kavli Institute of Nanoscience, TU Delft.
Tel: +31 (0)15 278 6064
Ms Ineke Boneschansker, Science Information Officer TU Delft.
Tel: +31 (0) 15 278 8499
Copyright © Delft University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








