Home > Press > A predilection for certain symmetries
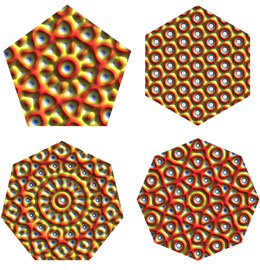 |
| Symmetry bears flowers: The Stuttgart-based researchers generate light patterns by superimposing several laser beams. Flower-shaped structures form in the laser patterns which act as a nucleus for order. They arise very rarely in the 7-fold pattern (bottom left) - therefore no materials with a 7-fold symmetry are found in nature. Image: Jules Mikhael, University of Stuttgart |
Abstract:
Researchers discover why atoms in solids show a preference for certain structures
A predilection for certain symmetries
Munich | Posted on March 30th, 2010Nature likes some symmetries, but dislikes others. Ordered solids often display a so-called 6-fold rotation symmetry. To achieve this kind of symmetry, the atoms in a plane surround themselves with six neighbours in an arrangement similar to that found in honeycombs. As opposed to this, ordered materials with 7-fold, 9-fold or 11-fold symmetries are never observed in nature. Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Metals Research, the University of Stuttgart and the TU Berlin discovered the reason for this when they tried to impose a 7-fold symmetry on a layer of charged colloidal particles using strong laser fields: the emergence of ordered structures requires the presence of specific sites where the corresponding order nucleates. Indeed, such nuclei are present in large numbers in exactly those structures for which nature shows a preference. In contrast, they only arise sporadically in patterns with 7-fold symmetry. (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Week of March 29, 2010)
The process involved here sounds unwieldy, but is, in fact, quite simple: a material has a 6-fold rotation symmetry if the arrangement of its atoms remains unchanged when it is rotated by 60 degrees - one sixth of a circle. The atoms in metals often order themselves in this way. However, more complicated structures with 5-fold, 8-fold or 10-fold rotation symmetry also exist. "It is surprising that materials with 7-fold, 9-fold or 11-fold symmetry have not yet been observed in nature," says Clemens Bechinger, fellow at the Max Planck Institute for Metals Research and Professor at the University of Stuttgart: "This is all the more astonishing in view of the fact that patterns with any rotation symmetry can be drawn without difficulty on paper." The question is, therefore, whether such materials have simply been overlooked up to now or whether nature has an aversion to certain symmetries.
This is the question that Clemens Bechinger has been investigating with his colleagues. "The answer is of interest to us both from a fundamental point of view but also because it could be helpful for tailoring materials with novel properties for technical applications," explains the physicist. The characteristics of a material are generally very dependent on its rotation symmetry. Graphite and diamond, for example, both consist of carbon atoms and differ solely in their crystal symmetry.
To produce materials with 7-fold symmetry, which do not actually exist in nature, the researchers resorted to a special trick: they superimposed seven laser beams and thereby generated a light pattern with 7-fold symmetry. They then introduced a layer of colloidal particles approximately three micrometers in diameter into the laser field. The effect of the electromagnetic field of the light pattern on the particles is akin to the formation of a mountain landscape, in which they tend to gravitate to the valleys. The colloidal particles, which repel each other because of their electric charges, attempt, in turn, to form a 6-fold symmetrical structure.
The researchers raise the profile of the light landscape by gradually increasing the intensity of the lasers. In this way, they exert increasing pressure on the colloidal particles to form a 7-fold symmetry instead of a 6-fold one. "This enables us to ascertain the laser intensity up to which the particles do not adept the 7-fold order and retain their 6-fold symmetry," says Jules Mikhael, the doctoral student working on the project.
In the same way, the physicists subjected the particles to a 5-fold light lattice and observed a clear difference: the particles clearly avoid a 7-fold symmetry and assume the 5-fold symmetry at relatively low laser intensities. Therefore, nature's rejection of 7-fold symmetries is also demonstrated in the model system created by the researchers in Stuttgart.
"What is crucial, however, is that our experiment also uncovers the reason why the particles stubbornly refuse to form a 7-fold structure," notes Clemens Bechinger. When the physicists increase the laser intensity, the particles initially only assume a 7-fold symmetry in very isolated places. Only when the intensity is further increased does the order spread to the entire sample. The researchers identified certain structures in the light pattern as the starting point for the 7-fold symmetry. These consist of a central point of light, which is surrounded by a ring of other light points and is, therefore, strongly reminiscent of a flower blossom.
"In the light pattern with 5-fold symmetry we find around 100 times more of these flower-shaped centres than in that with the 7-fold pattern," explains Michael Schmiedeberg. The density of these nuclei clearly plays the crucial role. The higher the density, the less force the researchers must exert to generate structures of the corresponding rotation symmetry. In this case, low light intensity is sufficient for the relevant order to spread from the centre.
The differences in the densities of the flower-shaped nuclei alone also explains why 8-fold and 10-fold symmetries arise in nature but 9-fold and 11-fold ones do not. "The result is astonishing because it involves a simple geometric argument," says Bechinger: "It is completely independent on the special nature of the interaction between the particles, and applies, therefore, both to our colloidal systems and to atomic systems."
The experiments explain, first, why it is no coincidence that materials with certain symmetries are not found in nature. Second, they demonstrate a concrete way, in which such structures can be made artificially in colloidal systems - that is with the help of external fields. This could be useful for the production of photonic crystals with unusual symmetries in which, for example, individual layers of colloids with 7-fold rotation symmetry are stacked on top of each other. Photonic crystals consist of microstructures, which affect light waves in a similar way to that in which crystal lattices affect electrons. Due to the higher rotation symmetry, the optical characteristics of 7-fold photonic crystals would be less dependent on the angle of incidence of a beam of light than the existing photonic crystals with 6-fold symmetry.
In addition to this, materials with unconventional symmetries have other interesting characteristics, for example very low frictional resistance. As a result they can reduce the friction between sliding parts e.g. in engines when applied as thin surface coatings. "Overall the search for materials with unusual rotation symmetries is of considerable interest," says Clemens Bechinger: "Our results can help to identify the particular symmetries that are worth looking for."
[PH/ClB]
Related links:
[1] more about unconventional symmetries www.pi2.uni-stuttgart.de/contact/index.php?article_id=127
Original work:
Jules Mikhael, Michael Schmiedeberg, Sebastian Rausch, Johannes Roth, Holger Stark, and Clemens Bechinger
Proliferation of anomalous symmetries in colloidal monolayers subjected to quasiperiodic light fields Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences early edition, March 29 to April 2
####
About Max Planck Society
The research institutes of the Max Planck Society perform basic research in the interest of the general public in the natural sciences, life sciences, social sciences, and the humanities. In particular, the Max Planck Society takes up new and innovative research areas that German universities are not in a position to accommodate or deal with adequately. These interdisciplinary research areas often do not fit into the university organization, or they require more funds for personnel and equipment than those available at universities. The variety of topics in the natural sciences and the humanities at Max Planck Institutes complement the work done at universities and other research facilities in important research fields. In certain areas, the institutes occupy key positions, while other institutes complement ongoing research. Moreover, some institutes perform service functions for research performed at universities by providing equipment and facilities to a wide range of scientists, such as telescopes, large-scale equipment, specialized libraries, and documentary resources.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Professor Clemens Bechinger
Physikalisches Institut,
University of Stuttgart
Tel.: +49 (0)711 685 65218
Copyright © Max Planck Society
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








