Home > Press > Argonne scientists to control attractive force for nanoelectromechanical systems
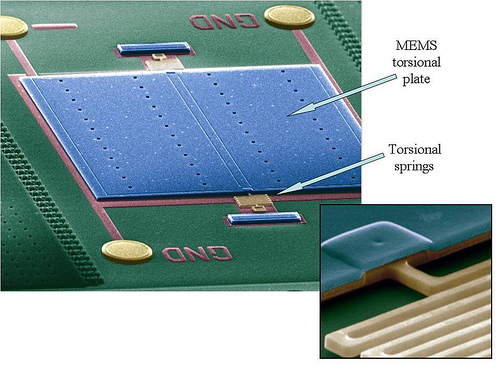 |
| MEMS used to detect the presence of the Casimir Force. Photo courtesy Argonne National Laboratory. |
Abstract:
DARPA to provide funding to quell Casimir force
Argonne scientists to control attractive force for nanoelectromechanical systems
Argonne, IL | Posted on January 4th, 2010Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory are developing a way to control the Casimir force, a quantum mechanical force which attracts objects when they are only a hundred nanometers apart.
"The Casimir force is so small that most experimentation has dealt simply with its characteristics," said Derrick Mancini, interim director of Argonne's Center for Nanoscale Materials. "If we can control this force or make it repulsive, it can have dramatic effects on the development of nanoelectromechanical systems."
Nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS) are nano-meter size mechanical devices that can be used for actuation or sensing at the nano-scale. Many NEMS devices are currently being developed for unique applications in sensing, telecommunications, signal processing, data storage and more. In the macro world, the Casimir force is so small that it can barely be detected, but at the nanoscale it becomes a quantum effect that scientists cannot currently control.
"As characteristic device dimensions shrink to the nanoscale, the effects of the attractive Casimir force become more pronounced, making very difficult to control nano-devices. This is a technological challenge that needs to be addressed before the full potential of NEMS devices can be demonstrated," scientist Daniel Lopez said. "The goal is to not only limit its attractive properties, but also to make it repulsive. A repulsive force acting at the nano-scale would allow engineers to design novel NEMS devices capable of frictionless motion through nanolevitation."
The approach to controlling this force involves nanostructuring the interacting surfaces to tune the effects of the Casimir force.
Argonne National Laboratory was recently selected by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) to develop mechanisms to control and manipulate the Casimir force. This program will be developed in close partnership with Indiana University - Purdue University Indianapolis, National Institute of Standards & Technology (NIST) and Los Alamos National Laboratory.
The Center for Nanoscale Materials at Argonne National Laboratory is one of the five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers (NSRCs), premier national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale, supported by the DOE Office of Science. Together, the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize and model nanoscale materials and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE's Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge, Sandia and Los Alamos national laboratories. For more information about the DOE NSRCs, please visit nano.energy.gov.
####
About Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America 's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Brock Cooper
630/252-5565
Copyright © Argonne National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
NEMS
![]() IEDM - CEA-Leti Will Present 11 Papers and Host Workshop on Disruptive Technologies for Data Management November 7th, 2018
IEDM - CEA-Leti Will Present 11 Papers and Host Workshop on Disruptive Technologies for Data Management November 7th, 2018
![]() UT engineers develop first method for controlling nanomotors: Breakthrough for nanotechnology as UT engineers develop first method for switching the mechanical motion of nanomotors September 21st, 2018
UT engineers develop first method for controlling nanomotors: Breakthrough for nanotechnology as UT engineers develop first method for switching the mechanical motion of nanomotors September 21st, 2018
![]() Nano-kirigami: 'Paper-cut' provides model for 3D intelligent nanofabrication July 13th, 2018
Nano-kirigami: 'Paper-cut' provides model for 3D intelligent nanofabrication July 13th, 2018
![]() One string to rule them all April 17th, 2018
One string to rule them all April 17th, 2018
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








