Home > Press > UCSB researchers discover living nanoscale 'necklace'
Abstract:
Researchers in physics and biology have made a discovery that could be instrumental in the production of miniaturized materials with many applications.
UC Santa Barbara researchers discover living nanoscale 'necklace'
Santa Barbara, CA – November 08, 2004
In an interdisciplinary endeavor at the University of California, Santa Barbara, a team of researchers in physics and biology have made a discovery at the nanoscale level that could be instrumental in the production of miniaturized materials with many applications. Dubbed a "living necklace," the finding was completely unexpected.
This discovery could influence the development of vehicles for chemical, drug, and gene delivery, enzyme encapsulation systems and biosensors, circuitry components, as well as templates for nanosized wires and optical materials. The findings are reported in the November 16 issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences and published online the week of November 8.
The collaborating labs are those of Cyrus Safinya, professor of materials and physics and faculty member of the Biomolecular Science & Engineering Program, and Leslie Wilson, professor of biochemistry in the Department of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology. The first author of the paper is Safinya's graduate student Daniel Needleman. Postdoctoral researchers Uri Raviv and Miguel Ojeda-Lopez from Safinya's group and Herbert Miller, a researcher in Wilson's group, completed the team.
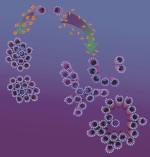
Schematics of higher-order assembly of nanometer-scale microtubules. Courtesy and Copyright © UCSB. Click to emlarge. |
The scientists studied microtubules from the brain tissue of a cow to understand the mechanisms leading to their assembly and shape. Microtubules are nanometer-scale hollow cylinders derived from cell cytoskeleton. In an organism, microtubules and their assembled structures are critical components in a broad range of cell functions -- from providing tracks for the transport of cargo to forming the spindle structure in cell division. Their functions include the transport of neurotransmitters in neurons. The mechanism of their assembly within an organism has been poorly understood.
In the paper, the researchers report the discovery of a new type of higher order assembly of microtubules. Positively-charged large, linear molecules (tri-, tetra- and penta-valent cations) resulted in a tightly bundled hexagonal grouping of microtubules – a result that was predicted. But unexpectedly, the scientists found that small, spherical divalent cations caused the microtubules to assemble into a "necklace." They discovered distinct linear, branched and loop shaped necklaces.
Safinya and Needleman commented that from a formal theoretical physics perspective, the living necklace phase is the first experimental realization of a new type of membrane where the long microtubule molecules are oriented in the same direction but can diffuse within the living membrane.
They explained that the living necklace bundle is highly dynamic and that thermal fluctuations will cause it to change shape.
The scientists envision applications based on both the tight bundle and living necklace phases. For example, metallization of necklace bundles with different sizes and shapes would yield nanomaterials with controlled optical properties.
A more original application is in the area of using the assemblies – encased by a lipid bilayer – as drug or gene carriers where each nanotube may contain a distinct chemical, as noted by the team. In delivery applications the shape of the bundle determines its property. For example, the linear necklace phase with its higher surface to volume ratio would have a larger contact area and a faster delivery rate compared to the tight bundle phase.
The work was performed using state-of-the-art synchrotron x-ray scattering techniques at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory combined with sophisticated electron and optical microscopy at UCSB.
Cyrus Safinya can be reached by e-mail at safinya@mrl.ucsb.edu
Daniel Needleman can be reached at 805-893-7922 or by e-mail at needle@mrl.ucsb.edu
Contact:
Gail Gallessich
gail.g@ia.ucsb.edu
805-893-7220
Copyright © UCSB
If you have a comment, please us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Department of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology
Department of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology
| Related News Press |
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Machines
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
![]() Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Giant nanomachine aids the immune system: Theoretical chemistry August 28th, 2020
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








