Home > Press > Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes
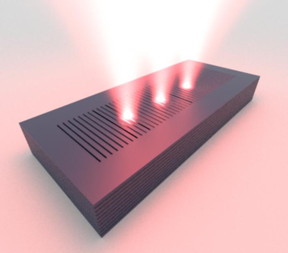 |
| Subwavelength grated waveguide supporting polariton droplets (visualization: Antonio Gianfrate, source: CNR Nanotec). CREDIT CNR Nanotec |
Abstract:
Scientists from CNR Nanotec in Lecce and the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw used a new generation of semiconductor photonic gratings to optically tailor complexes of quantum droplets of light that became bound together into macroscopic coherent states. The research underpins a new method to simulate and explore interactions between artificial atoms in a highly reconfigurable manner, using optics. The results have been published in the prestigious journal “Nature Physics”
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes
Warsaw, Poland | Posted on March 8th, 2024Condensed matter systems and photonic technologies are regularly used by researchers to create microscale platforms that can simulate the complex dynamics of many interacting quantum particles in a more accessible setting. Some examples include ultracold atomic ensembles in optical lattices, superconducting arrays, and photonic crystals and waveguides. In 2006 a new platform emerged with the demonstration of macroscopically coherent quantum fluids of exciton-polaritons to explore many-body quantum phenomena through optical techniques.
When a piece semiconductor is placed between two mirrors – an optical microresonator – the electronic excitations within can become strongly influenced by photons trapped between the mirrors. The resulting new bosonic quantum particles, known as exciton-polaritons (or polaritons for short), can under the right circumstances undergo a phase transition into a nonequilibrium Bose-Einstein condensate and form a macroscopic quantum fluid or a droplet of light. Quantum fluids of polaritons have many salient properties, one being that they are optically configurable and readable, permitting easy measurements of the polariton dynamics. This is what makes them so advantageous to simulate many-body physics.
Polariton condensates must be continuously optically pumped with external lasers to replenish particles, otherwise the condensate dissipates within picoseconds. However, the harder you pump the condensate the more energetic it becomes due to repulsive interparticle forces, leading to particles escaping the condensate and subsequent decay of spatial correlations. This is a fundamental problem for optically programmable polariton simulators. Scientists needed to come up with a way to make the condensate more stable and long lived, while still being optically pumped.
Scientists from CNR Nanotec in Lecce and the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw, achieved this goal using a new generation of semiconductor photonic gratings. In their paper titled "Reconfigurable quantum fluid molecules of bound states in the continuum", published in Nature Physics, they used subwavelength properties of the photonic grating to imbue polaritons with new properties. First, the polaritons could be driven to condense into an ultralong lifetime state known as bound state in the continuum (BIC). The fascinating thing about BICs is that they are mostly non-radiative due to symmetry enforced protection from the outside continuum of photonic modes. Second, the polaritons obtained a negative effective mass due to the dispersion relation coming from the grating. This meant that the pumped polaritons could not escape so easily through normal decay channels anymore. Now, the researchers possessed polariton fluids that were both extremely long lived and safely confined using only optical techniques.
Combined, these mechanisms allowed Antonio Gianfrate and Danielle Sanvitto at CNR Nanotec in Lecce to optically pump multiple polariton droplets that could interact and hybridize into macroscopic complexes. They could tailor and reversibly configure molecular arrangements and chains using this new form of artificial atoms: condensates of negative-mass BIC polaritons. The BIC property provided polaritons with much longer lifetimes whereas the negative mass property caused them to become optically trapped. The findings were supported by a BIC Dirac-polariton theory developed between Helgi Sigurdsson (University of Warsaw), Hai Chau Nguyen (University of Siegen, Germany), and Hai Son Nguyen (Univ Lyon, France).
The ultimate advantage of the platform is that the artificial quantum complexes can be all-optically programmed yet they retain very high lifetimes because of their protection from the continuum. This could lead to a new venture into optically programmable large-scale quantum fluids defined by unprecedented coherence scales and stability for structured nonlinear lasing and polariton-based simulation of complex systems.
“There are still several interesting ways to explore in this artificial polaritonic Dirac system. As an example, the coupling mechanism between polariton droplets along and perpendicular to the grating direction is very different. Along the waveguide, polaritons are effectively negative mass particles strongly bound to their pump spot. Perpendicular to the waveguide they move as positive mass particles undergoing ballistic transport. The mixture of these two mechanisms opens a new window to look at emergent behaviours of synchrony and pattern formation in structured polariton quantum fluids” concludes Helgi Sigurðsson from the Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw.
An international team of scientists conducted research supported by the National Science Center grant (2022/45/P/ST3/00467) co-funded by the European Union Framework Programme for Research and Innovation Horizon 2020 under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement (No. 945339).
####
About University of Warsaw, Faculty of Physics
Physics and astronomy at the University of Warsaw appeared in 1816 as part of the then Faculty of Philosophy. In 1825, the Astronomical Observatory was established. Currently, the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw consists of the following institutes: Experimental Physics, Theoretical Physics, Geophysics, the Department of Mathematical Methods and the Astronomical Observatory. The research covers almost all areas of modern physics, on scales from quantum to cosmological. The Faculty's research and teaching staff consists of over 250 academic teachers. About 1,100 students and over 170 doctoral students study at the Faculty of Physics UW. The University of Warsaw is among the 150 best universities in the world educating in the field of physics according to the Shanghai’s Global Ranking of Academic Subjects.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Agata Meissner
University of Warsaw, Faculty of Physics
Office: 225-532-573
@physics_UW
Expert Contact
Dr Helgi Sigurdsson
Faculty of Physics University of Warsaw
Office: +48 22 55 32 765
@physics_UW
Copyright © University of Warsaw, Faculty of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Tumor microenvironment dynamics: the regulatory influence of long non-coding RNAs April 25th, 2025
Tumor microenvironment dynamics: the regulatory influence of long non-coding RNAs April 25th, 2025
![]() Ultrafast plasmon-enhanced magnetic bit switching at the nanoscale April 25th, 2025
Ultrafast plasmon-enhanced magnetic bit switching at the nanoscale April 25th, 2025
![]() Next-generation drug delivery innovation! DGIST develops precision therapeutics using exosomes April 25th, 2025
Next-generation drug delivery innovation! DGIST develops precision therapeutics using exosomes April 25th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
Quantum Physics
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Physics
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
Superconductivity
![]() Researchers observe “locked” electron pairs in a superconductor cuprate August 16th, 2024
Researchers observe “locked” electron pairs in a superconductor cuprate August 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Tumor microenvironment dynamics: the regulatory influence of long non-coding RNAs April 25th, 2025
Tumor microenvironment dynamics: the regulatory influence of long non-coding RNAs April 25th, 2025
![]() Ultrafast plasmon-enhanced magnetic bit switching at the nanoscale April 25th, 2025
Ultrafast plasmon-enhanced magnetic bit switching at the nanoscale April 25th, 2025
![]() Next-generation drug delivery innovation! DGIST develops precision therapeutics using exosomes April 25th, 2025
Next-generation drug delivery innovation! DGIST develops precision therapeutics using exosomes April 25th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Tumor microenvironment dynamics: the regulatory influence of long non-coding RNAs April 25th, 2025
Tumor microenvironment dynamics: the regulatory influence of long non-coding RNAs April 25th, 2025
![]() Ultrafast plasmon-enhanced magnetic bit switching at the nanoscale April 25th, 2025
Ultrafast plasmon-enhanced magnetic bit switching at the nanoscale April 25th, 2025
![]() Next-generation drug delivery innovation! DGIST develops precision therapeutics using exosomes April 25th, 2025
Next-generation drug delivery innovation! DGIST develops precision therapeutics using exosomes April 25th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Tumor microenvironment dynamics: the regulatory influence of long non-coding RNAs April 25th, 2025
Tumor microenvironment dynamics: the regulatory influence of long non-coding RNAs April 25th, 2025
![]() Ultrafast plasmon-enhanced magnetic bit switching at the nanoscale April 25th, 2025
Ultrafast plasmon-enhanced magnetic bit switching at the nanoscale April 25th, 2025
![]() Next-generation drug delivery innovation! DGIST develops precision therapeutics using exosomes April 25th, 2025
Next-generation drug delivery innovation! DGIST develops precision therapeutics using exosomes April 25th, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Tumor microenvironment dynamics: the regulatory influence of long non-coding RNAs April 25th, 2025
Tumor microenvironment dynamics: the regulatory influence of long non-coding RNAs April 25th, 2025
![]() Ultrafast plasmon-enhanced magnetic bit switching at the nanoscale April 25th, 2025
Ultrafast plasmon-enhanced magnetic bit switching at the nanoscale April 25th, 2025
![]() Next-generation drug delivery innovation! DGIST develops precision therapeutics using exosomes April 25th, 2025
Next-generation drug delivery innovation! DGIST develops precision therapeutics using exosomes April 25th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Bringing the power of tabletop precision lasers for quantum science to the chip scale December 13th, 2024
Bringing the power of tabletop precision lasers for quantum science to the chip scale December 13th, 2024
![]() Researchers succeed in controlling quantum states in a new energy range December 13th, 2024
Researchers succeed in controlling quantum states in a new energy range December 13th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Researchers succeed in controlling quantum states in a new energy range December 13th, 2024
Researchers succeed in controlling quantum states in a new energy range December 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








