Home > Press > A new strategy to create 2D magnetic order
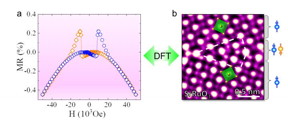 |
| (a) The transport measurements. (b) An atomically resolved electron microscopy image showing the anionic and cationic configuration of SrRuO3 grain boundary. The first principles calculations bridge the structure-property relation. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Grain boundaries, which are consist of periodic arrangement of structural units and generally recognized as a two-dimensional "phase", can exhibit novel properties that are not existed in the intrinsic bulk crystal. The altered continuity of atomic bonding at grain boundaries cause local chemical environment dramatically change at a few unit cells, subsequently alter local electrical activity, magnetic order or other physical properties. The effects of grain boundary on properties is even more significant in the complex oxides due to the substantial interactions between lattice and other order parameters. Therefore, such an inhomogeneity of materials with grain boundary may dominate the entire response in nanoscale devices and have garnered particular interest in designing novel functional devices.
A new strategy to create 2D magnetic order
Beijing, China | Posted on April 10th, 2020The nature of structural defects is determined by the atomic arrangements. Correlating the properties of single defect-based device with its specific atomic structure is vital and prerequisite for the device application. However, experimentally revealing such a structure-property relation is very challenging due to the atomic-size and chemical and structural complexity of defects, especially for the perovskite oxides that contain multiple elements.
In a new research article published in the Beijing-based National Science Review, scientists at Peking university, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Tianjin University present atomic mechanism of spin-valve magnetoresistance at the asymmetry SrRuO3 grain boundary. The asymmetry atomic structure is very different from the common assumption based on prototype perovskite SrTiO3. The transport measurements exhibit the spin-valve magnetoresistance for the as fabricated centimeter-size and sub-nm-width Σ5(310) SrRuO3 grain boundary. Advanced scanning transmission electron microscopy and spectroscopy reveal its atomic arrangements based on which the first principles calculations reveal its electronic properties. Scientists find that owing to the Ru-O octahedron distortion near the asymmetric grain boundary, Ru d orbital reconstructs and results in reduction of magnetic moments and change of spin polarization along the grain boundary, forming a magnetic/nonmagnetic/magnetic junction. The calculations bridge the atomic structure with transport properties.
"Our findings can help us to understand the past transport properties such as the negative magnetoresistance and absence of tunneling magnetoresistance at the SrRuO3 grain boundary, and also predict new effects of SrRuO3 grain boundary such as the interfacial magnetoelectric coupling when SrRuO3 is used as a bottom electrode for growth of ferroelectric thin films." Prof. Peng Gao said, "In a broader perspective, control of defect structure at atomic scale can realize peculiar physical properties, providing us a new strategy to design devices with new low-dimensional magnetic properties by using boundary engineering."
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFA0300804), National Equipment Program of China (ZDYZ2015-1), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51672007 and 11974023), the Key-Area Research and Development Program of GuangDong Province (No. 2018B030327001?2018B010109009) and "2011 Program" Peking-Tsinghua-IOP Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter. Project was also supported by State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha, China
####
About Science China Press
The National Science Review is the first comprehensive scholarly journal released in English in China that is aimed at linking the country's rapidly advancing community of scientists with the global frontiers of science and technology. The journal also aims to shine a worldwide spotlight on scientific research advances across China.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Peng Gao
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








