Home > Press > KIST unveils the mystery of van der Waals magnets, a material for future semiconductors: Overcoming the limits of current magnetic materials, giving hope for development of next-generation semiconductors
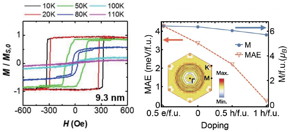 |
| The team conducted an experiment in which they observed the material while controlling the number of electrons, leading them to discover changes in the properties of FGT. The team proved that the magnetic anisotropy, which describes how the material's magnetic properties change depending on the direction, contributed to such changes. CREDIT Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) |
Abstract:
Drs. Chaun Jang, Jun Woo Choi, and Hyejin Ryu of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Lee Byung Gwon) have announced that their team at KIST's Center for Spintronics successfully controlled the magnetic properties of FGT (Fe3GeTe2) in a joint research project with Dr. Se Young Park and his team at the Center for Correlated Electron Systems at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS). Fe3GeTe2 has recently attracted attention as a material for next-generation spintronic semiconductors.
KIST unveils the mystery of van der Waals magnets, a material for future semiconductors: Overcoming the limits of current magnetic materials, giving hope for development of next-generation semiconductors
Sejong, Korea | Posted on February 14th, 2020*Named by combining the terms "spin" and "electronics," "spintronics" is a new field in electronic engineering that aims to replace conventional silicon semiconductors by utilizing electron spin, a quantum property of electrons.
Van der Waals materials, also known as two-dimensional (2D) materials, are layered materials composed of planes that are attached to each other via a weak van der Waals interaction. These include various materials such as graphene and molybdenum disulfide. When combined with other 2D materials, they can create new materials that show previously undiscovered properties. This is why 2D materials, which have a variety of properties, such as superconductivity, semi-conductivity, and metallicity have been the subject of so many studies.
In 2017, 2D van der Waals materials that show magnetic properties were discovered, stimulating research projects and studies all around the world. However, most van der Waals magnetic materials have some constraints in terms of spintronics application because of their low Curie temperature** and high coercivity,*** making them unsuitable for use in certain devices.
** Curie temperature: a transition temperature point where a ferromagnetic material changes to a paramagnetic one or vice versa.
*** Coercivity: the intensity of magnetic field required to reduce the magnetic flux density of a ferromagnetic material to zero after the magnetism of that material has been saturated.
A number of studies have been done on FGT, a recently discovered van der Waals material with a layered structure. The joint KIST-IBS research team discovered an efficient scheme for controlling the properties of FGT. The team conducted an experiment in which they observed the material while controlling the number of electrons, leading them to discover changes in the properties of FGT. The team proved that the magnetic anisotropy,**** which describes how the material's magnetic properties change depending on the direction, contributed to such changes.
**** Magnetic anisotropy: This refers to the directional dependence of a material's magnetic properties on a crystallographic or geometric structure. Depending on such structures, a material can have easy or hard magnetization directions.
The research results revealed the origin of the changes in the FGT magnetic properties, thus presenting a possible method of efficiently controlling the properties of 2D magnetic materials. Furthermore, the research team announced that by potentially controlling the properties of single-atom-thick van der Waals magnetic materials, the development of spintronic devices which operate 100-times faster than current silicon-based electronic device, could be accelerated.
Dr. Hyejin Ryu of KIST said, "We started this study to discover the magnetic properties of van der Waals materials and apply such properties to spintronic devices." She added, "Further development of new materials for semiconductors with various properties will be possible through the use of van der Waals magnetic materials and other van der Waals materials based heterostructures."
###
This major KIST research project was conducted with the support of the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Choi Kiyoung) as part of the Creative Convergence Research Project (CAP) for the purpose of laying the foundation for global, cross-border cooperation. This work was also supported by the US DOE-BES (Lawrence Berkeley National Lab), and the Division of Materials Science and Engineering (Brookhaven National Lab). The research results were published in the most recent issue of Nano Letters (IF:12.279, JCR Rank: 5.743%).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kim, Do-Hyun
82-295-86344
Copyright © National Research Council of Science & Technology(NST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








