Home > Press > In leap for quantum computing, silicon quantum bits establish a long-distance relationship: Princeton scientists demonstrate that two silicon quantum bits can communicate across relatively long distances in a turning point for the technology
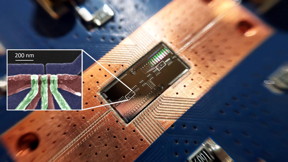 |
| Researchers at Princeton University have made an important step forward in the quest to build a quantum computer using silicon components, which are prized for their low cost and versatility compared to the hardware in today's quantum computers. The team showed that a silicon-spin quantum bit (shown in the box) can communicate with another quantum bit located a significant distance away on a computer chip. The feat could enable connections between multiple quantum bits to perform complex calculations. CREDIT Image by Felix Borjans, Princeton University |
Abstract:
Imagine a world where people could only talk to their next-door neighbor, and messages must be passed house to house to reach far destinations.
In leap for quantum computing, silicon quantum bits establish a long-distance relationship: Princeton scientists demonstrate that two silicon quantum bits can communicate across relatively long distances in a turning point for the technology
Princeton, NJ | Posted on December 27th, 2019Until now, this has been the situation for the bits of hardware that make up a silicon quantum computer, a type of quantum computer with the potential to be cheaper and more versatile than today's versions.
Now a team based at Princeton University has overcome this limitation and demonstrated that two quantum-computing components, known as silicon "spin" qubits, can interact even when spaced relatively far apart on a computer chip. The study was published in the journal Nature.
"The ability to transmit messages across this distance on a silicon chip unlocks new capabilities for our quantum hardware," said Jason Petta, the Eugene Higgins Professor of Physics at Princeton and leader of the study. "The eventual goal is to have multiple quantum bits arranged in a two-dimensional grid that can perform even more complex calculations. The study should help in the long term to improve communication of qubits on a chip as well as from one chip to another."
Quantum computers have the potential to tackle challenges beyond the capabilities of everyday computers, such as factoring large numbers. A quantum bit, or qubit, can process far more information than an everyday computer bit because, whereas each classical computer bit can have a value of 0 or 1, a quantum bit can represent a range of values between 0 and 1 simultaneously.
To realize quantum computing's promise, these futuristic computers will require tens of thousands of qubits that can communicate with each other. Today's prototype quantum computers from Google, IBM and other companies contain tens of qubits made from a technology involving superconducting circuits, but many technologists view silicon-based qubits as more promising in the long run.
Silicon spin qubits have several advantages over superconducting qubits. The silicon spin qubits retain their quantum state longer than competing qubit technologies. The widespread use of silicon for everyday computers means that silicon-based qubits could be manufactured at low cost.
The challenge stems in part from the fact that silicon spin qubits are made from single electrons and are extremely small.
"The wiring or 'interconnects' between multiple qubits is the biggest challenge towards a large scale quantum computer," said James Clarke, director of quantum hardware at Intel, whose team is building silicon qubits using using Intel's advanced manufacturing line, and who was not involved in the study. "Jason Petta's team has done great work toward proving that spin qubits can be coupled at long distances."
To accomplish this, the Princeton team connected the qubits via a "wire" that carries light in a manner analogous to the fiber optic wires that deliver internet signals to homes. In this case, however, the wire is actually a narrow cavity containing a single particle of light, or photon, that picks up the message from one qubit and transmits it to the next qubit.
The two qubits were located about half a centimeter, or about the length of a grain of rice, apart. To put that in perspective, if each qubit were the size of a house, the qubit would be able to send a message to another qubit located 750 miles away.
The key step forward was finding a way to get the qubits and the photon to speak the same language by tuning all three to vibrate at the same frequency. The team succeeded in tuning both qubits independently of each other while still coupling them to the photon. Previously the device's architecture permitted coupling of only one qubit to the photon at a time.
"You have to balance the qubit energies on both sides of the chip with the photon energy to make all three elements talk to each other," said Felix Borjans, a graduate student and first author on the study. "This was the really challenging part of the work."
Each qubit is composed of a single electron trapped in a tiny chamber called a double quantum dot. Electrons possess a property known as spin, which can point up or down in a manner analogous to a compass needle that points north or south. By zapping the electron with a microwave field, the researchers can flip the spin up or down to assign the qubit a quantum state of 1 or 0.
"This is the first demonstration of entangling electron spins in silicon separated by distances much larger than the devices housing those spins," said Thaddeus Ladd, senior scientist at HRL Laboratories and a collaborator on the project. "Not too long ago, there was doubt as to whether this was possible, due to the conflicting requirements of coupling spins to microwaves and avoiding the effects of noisy charges moving in silicon-based devices. This is an important proof-of-possibility for silicon qubits because it adds substantial flexibility in how to wire those qubits and how to lay them out geometrically in future silicon-based 'quantum microchips.'"
The communication between two distant silicon-based qubits devices builds on previous work by the Petta research team. In a 2010 paper in the journal Science, the team showed it is possible to trap single electrons in quantum wells. In the journal Nature in 2012, the team reported the transfer of quantum information from electron spins in nanowires to microwave-frequency photons, and in 2016 in Science they demonstrated the ability to transmit information from a silicon-based charge qubit to a photon. They demonstrated nearest-neighbor trading of information in qubits in 2017 in Science. And the team showed in 2018 in Nature that a silicon spin qubit could exchange information with a photon.
Jelena Vuckovic, professor of electrical engineering and the Jensen Huang Professor in Global Leadership at Stanford University, who was not involved in the study, commented: "Demonstration of long-range interactions between qubits is crucial for further development of quantum technologies such as modular quantum computers and quantum networks. This exciting result from Jason Petta's team is an important milestone towards this goal, as it demonstrates non-local interaction between two electron spins separated by more than 4 millimeters, mediated by a microwave photon. Moreover, to build this quantum circuit, the team employed silicon and germanium - materials heavily used in the semiconductor industry."
###
In addition to Borjans and Petta, the following contributed to the study: Xanthe Croot, a Dicke postdoctoral fellow; associate research scholar Michael Gullans; and Xiao Mi, who earned his Ph.D. at Princeton in Petta's group and is now a research scientist at Google.
The study was funded by Army Research Office (grant W911NF-15-1-0149) and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation's EPiQS Initiative (grant GBMF4535).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Catherine Zandonella
609-258-0541
@Princeton
Copyright © Princeton University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum communication
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








