Home > Press > Research Reveals Exotic Quantum States in Double-Layer Graphene: Findings shed new light on the nature of electron interactions in quantum systems and establish a potential new platform for future quantum computers
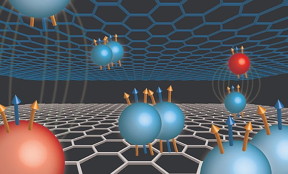 |
| A new type quasiparticle is discovered in graphene double-layer structure. This so-called composite fermion consists of one electron and two different types of magnetic flux, illustrated as blue and gold colored arrows in the figure. Composite fermions are capable of forming pairs, such unique interaction lead to experimental discovery of unexpected new quantum Hall phenomena. Michelle Miller and Jia Li/Brown University |
Abstract:
Researchers from Brown and Columbia Universities have demonstrated previously unknown states of matter that arise in double-layer stacks of graphene, a two-dimensional nanomaterial. These new states, known as the fractional quantum Hall effect, arise from the complex interactions of electrons both within and across graphene layers.
Research Reveals Exotic Quantum States in Double-Layer Graphene: Findings shed new light on the nature of electron interactions in quantum systems and establish a potential new platform for future quantum computers
New York, NY | Posted on June 26th, 2019“The findings show that stacking 2D materials together in close proximity generates entirely new physics,” said Jia Li, assistant professor of physics at Brown, who initiated this work while a post-doc at Columbia working with Cory Dean, professor of physics, and Jim Hone, professor of mechanical engineering. “In terms of materials engineering, this work shows that these layered systems could be viable in creating new types of electronic devices that take advantage of these new quantum Hall states.”
A new type quasiparticle is discovered in graphene double-layer structure. This so-called composite fermion consists of one electron and two different types of magnetic flux, illustrated as blue and gold colored arrows in the figure. Composite fermions are capable of forming pairs, such unique interaction lead to experimental discovery of unexpected new quantum Hall phenomena.
Michelle Miller and Jia Li/Brown University
The research is published in the journal Nature Physics.
Importantly, says Hone, Wang Fong-Jen Professor of Mechanical Engineering at Columbia Engineering, several of these new quantum Hall states “may be useful in making fault-tolerant quantum computers.”
The Hall effect emerges when a magnetic field is applied to a conducting material in a perpendicular direction to a current flow. The magnetic field causes the current to deflect, creating a voltage in the transverse direction, called the Hall voltage. The strength of the Hall voltage increases with the strength of the magnetic field. The quantum version of the Hall effect was first discovered in experiments performed in 1980 at low temperatures and strong magnetic fields. The experiments showed that rather than increasing smoothly with magnetic field strength, the Hall voltage increases in step-wise (or quantized) fashion. These steps are integer multiples of fundamental constants of nature and are entirely independent of the physical makeup of the material used in the experiments. The discovery was awarded the 1985 Nobel Prize in Physics.
A few years later, researchers working at temperatures near absolute zero and with very strong magnetic fields found new types of quantum Hall states in which the quantum steps in Hall voltage correspond to fractional numbers, hence the name fractional quantum Hall effect. The discovery of the fractional quantum Hall effect won another Nobel Prize, in 1998. Theorists later posited that the fractional quantum Hall effect is related to the formation of quasi-particles called composite fermions. In this state, each electron combines with a quantum of magnetic flux to form a composite fermion carrying a fraction of an electron charge giving rise to the fractional values in Hall voltage.
The composite fermion theory has been successful in explaining a myriad of phenomena observed in single quantum well systems. This new research used double-layer graphene to investigate what happens when two quantum wells are brought close together. Theory had suggested that the interaction between two layers would lead to a new type of composite fermion, but this had never been observed in experiment.
For the experiments, the team built on many years of work at Columbia to improve the quality of graphene devices, creating ultra-clean devices entirely from atomically flat 2D materials. The core of the structure consists of two graphene layer separated by a thin layer of hexagonal boron nitride as an insulating barrier. The double-layer structure is encapsulated by hexagonal boron nitride as a protective insulator, and graphite as a conductive gate to change the charge carrier density in the channel.
“Once again the incredible versatility of graphene has allowed us to push the boundaries of device structures beyond what was previously possible.” says Dean, a professor of physics at Columbia University. “The precision and tunability with which we can make these devices is now allowing us to explore an entire realm of physics that was just recently thought to be totally inaccessible.”
The graphene structures were then exposed to strong magnetic fields—millions of times stronger than Earth’s magnetic field. The research produced a range of fractional quantum Hall states, some of which demonstrate excellent agreement with the composite fermion model, and some that had never been predicted or seen.
“Apart from the interlayer composite fermions, we observed other features that cannot be explained within the composite fermion model,” said Qianhui Shi, the paper’s co-first author and postdoctoral researcher at Columbia. "A more careful study revealed that, to our surprise, these new states result from pairing between composite fermions. Pairing interaction between adjacent layers and within the same layer give rise to a variety of new quantum phenomena, making double-layer graphene an exciting platform to study.”
“Of particular interest,” says Hone, “are several new states that have the potential of hosting non-Abelian wave functions—states that don’t quite fit the traditional composite fermion model.” In non-Abelian states, electrons maintain a kind of “memory” of their past positions relative to each other. That has potential in enabling quantum computers that do not require error correction, which is currently a major stumbling block in the field.
“These are the first new candidates for non-Abelian states in 30 years,” Dean said. “It’s really exciting to see new physics emerge from our experiments.”
About the Study
The study is titled “Pairing states of composite fermions in double-layer graphene.”
The authors are: Jia Li, Qianhui Shi, Yihang Zeng, Kenji Watanabe, Takashi Taniguchi, James Hone and Cory Dean.
The study was supported by the National Science Foundation (DMR-1507788), the David and Lucille Packard Foundation, and the Department of Energy (DE-SC0016703).
The magnetic field experiments were done at the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory in Tallahassee, Florida, a nationally funded user facility.
The authors declare no competing interests.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Holly Evarts, Director of Strategic Communications and Media Relations, Columbia Engineering
212-854-3206 (o), 347-453-7408 (c),
Kevin Stacey, Senior Writer, Physical Sciences, Brown University
401-863-3766 (o); 401-447-3800,
Copyright © Columbia University School of Engineering and Applied Science
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








