Home > Press > Straightforward biosynthesis of functional bulk nanocomposites
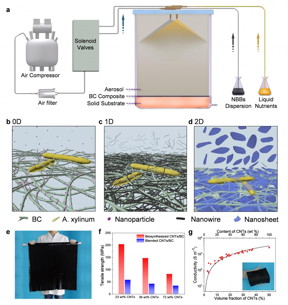 |
| The biosynthesis strategy of functional bulk nanocomposites. a, Scheme of the bioreactor. Aerosols of liquid nutrient and nanoscale building block suspensions were fed into the bioreactor with filtered compressed air, which was controlled by an automatic control system. b to d, Schematic illustration of the formation uniform BC-based nanocomposites with 0D nanoparticles (b), 1D nanotubes or nanowires (c), and 2D nanosheets (d). e, Photograph of a large-sized CNTs/BC pellicle with a volume of 800×800×8 mm3. f, Comparison of the tensile strength of the biosynthesized CNTs/BC nanocomposites with blended CNTs/BC nanocomposites. g, Electrical conductivity of the CNTs/BC films as a function of CNTs volume and weight fraction. Reprinted with permission of Oxford University Press. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Interest in constructing bulk nanocomposite materials from biosourced and renewable nanoscale building blocks is growing. As a crystalline cellulosic polymer, cellulose is the most abundant biosourced and renewable polymeric material on earth, which can be extracted from plant or produced by bacteria. Bacterial cellulose (BC) nanofibrils possess a high tensile strength as high as steel and Kevlar and spontaneously formed a robust three-dimensional (3D) nanofibrous network, which makes it an ideal platform for design of functional bulk nanocomposites. BC and its nanocomposites have been widely used in many fields, including acoustic membrane, electron device, energy storage and catalyst. However, the conventional process for fabricating uniform BC nanocomposites involved the disintegration of 3D network structure for solution processing, which seriously impaired the mechanical performance of the nanocomposites. So, strategies without disintegration the 3D network structure are core important for constructing bulk BC based nanocomposites.
Straightforward biosynthesis of functional bulk nanocomposites
Beijing, China | Posted on February 5th, 2019In response to this challenge, recently, researchers led by Professor Shu-Hong Yu from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) successfully developed a general and scalable biosynthesis strategy, which involves simultaneous growth of cellulose nanofibrils through microbial fermentation and co-deposition of various kinds of nanoscale building blocks (NBBs) through aerosol feeding on solid culture substrates (Fig. 1).
This method overcome the diffusion limitation of nanoscale units from the liquid medium to the upper surface layer of new-grown BC, through which, researchers successfully prepared a series of bulk nanocomposites of BC and nanoscale building blocks of different dimension, shapes, and sizes (Fig.1 b-d). Particularly, the method can be easily scaled up for potentially industrial applications by using large reactors and increasing the number of nozzles (Fig. 1c).
To demonstrate the merit and uniqueness of this method, researchers tuned the content of CNTs in a wide range from 1.5 wt% to 75 wt% by changing the concentration of CNTs suspensions. Note that conventional fabrication method for CNTs nanocomposites that requires the mixing of CNTs dispersions with polymer solutions is only applicable to prepare polymer nanocomposites with low CNTs (< 10 wt%), as it is extremely difficult to homogeneously disperse high-concentration CNTs in polymeric hosts. To further demonstrate the advantages of the biosynthesis strategy for preparing mechanically reinforced nanocomposites, CNTs/BC nanocomposite films were also prepared for comparison by blending of CNTs and disintegrated BC suspensions. Both the tensile strength and Young's modulus of the biosynthesized CNTs/BC nanocomposites were remarkably higher than that blended samples. As a result, the biosynthesized CNTs/BC nanocomposites achieve simultaneously an extremely high mechanical strength and electrical conductivity (Fig. 1g, h), which is of crucial importance for practical application.
This general and scalable biosynthesis strategy makes it possible for simultaneous growth of cellulose nanofibrils through microbial fermentation and co-deposition of various kinds of nanoscale building blocks through aerosol feeding on solid culture substrates. "By upgrading the state-of-the-art production line that produces pure bacterial cellulose pellicles, industrial-scale production of these bulk nanocomposite materials for practical applications can be expected in the near future.", the scientists forecast.
###
This research received funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Shu-Hong Yu
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








