Home > Press > Graphene controls surface magnetism at room temperature
 |
Abstract:
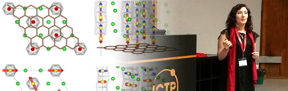
Typically research has focused on the effects induced by different materials in graphene. Convinced that this is only half the story, Dr Zeila Zanolli turned the tables to look at the proximity effects of graphene on magnetic semiconducting substrates. Using first principles calculations she observes a switching of internal spin alignment from antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic. Persisting close to room temperature, her findings could find applications in magnetic memories or spin filters.
Graphene controls surface magnetism at room temperature
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on October 8th, 2018More information or direct interview with the researcher can be organised upon request. Best.
Story: In a refreshing change of perspective, theoretical physicist Dr Zeila Zanolli has looked at the proximity effects of graphene on a magnetic semiconducting substrate, finding it to affect the substrate’s magnetism down to several layers below the surface. Her paper was published on 5 October in Physical Review B. She was also one of three recipients of the first MaX Prize for frontier research in computational materials science.
Interface physics is the study of the interactions that take place at the junction of two or more materials when brought into contact. Interfaces have always existed, but it is only with advances in the observation and manipulation of matter at the nanoscale that it has become possible to explore the unique phenomena they are home to. Since the advent of graphene, the attention of the research community has been focused on how other materials can be used to imprint new properties onto this intoxicatingly versatile material. In the belief that this is only half the story, Dr Zeila Zanolli of the ICN2 Theory and Simulation Group led by Prof. Pablo Ordejón has instead looked at the effects graphene has on the substrate.
Published in Physical Review B, her latest work shows how, when some oxide materials are brought into contact with graphene, reactions at the interface can lead their magnetic state to become altered. Investigating further, Dr Zanolli also observed these effects to be present several atomic layers below the interface itself.
Specifically, the graphene induces a magnetic softening in the oxide substrate, switching its internal spin alignment from antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic. This state should persist close to room temperature, leading to applications in magnetic memories or spin filters.
The research was conducted using two flagship codes from the MaX European Center of Excellence: the SIESTA package co-created by Prof. Pablo Ordejón and selected by the Journal of Physics as one of the most important breakthroughs published in its pages, and FLEUR developed at Forschungszentrum Jülich. It was also awarded one of the first MaX Prizes for flagship code applications, announced earlier this year at the MaX International Conference (ICTP Trieste). The MaX European Center of Excellence works at the frontiers of high performance computing (HPC) technologies to enable the best use and evolution of HPC for materials research and innovation.
Article reference:
Z. Zanolli, C. Niu, G. Bihlmayer, Y. Mokrousov, P. Mavropoulos, M.J. Verstraete, S. Blügel. Hybrid quantum anomalous Hall effect at graphene-oxide interfaces. Physical Review B. 00, 005400 (2018) DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.00.005400
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Rachel Spencer
Copyright © ICN2
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








