Home > Press > Switching with molecules: Molecular switch will facilitate the development of pioneering electro-optical devices
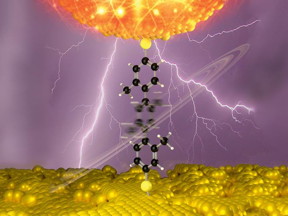 |
| A research team at the Technical University of Munich has developed molecular nanoswitches that can be toggled between two structurally different states using an applied voltage. They can serve as the basis for a pioneering class of devices that could replace silicon-based components with organic molecules. CREDIT Yuxiang Gong / TUM / Journal of the American Chemical Society |
Abstract:
A research team led by physicists at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has developed molecular nanoswitches that can be toggled between two structurally different states using an applied voltage. They can serve as the basis for a pioneering class of devices that could replace silicon-based components with organic molecules.
Switching with molecules: Molecular switch will facilitate the development of pioneering electro-optical devices
Munich, Germany | Posted on May 25th, 2018The development of new electronic technologies drives the incessant reduction of functional component sizes. In the context of an international collaborative effort, a team of physicists at the Technical University of Munich has successfully deployed a single molecule as a switching element for light signals.
"Switching with just a single molecule brings future electronics one step closer to the ultimate limit of miniaturization," says nanoscientist Joachim Reichert from the Physics Department of the Technical University of Munich.
Different structure - different optical properties
The team initially developed a method that allowed them to create precise electrical contacts with molecules in strong optical fields and to control them using an applied voltage. At a potential difference of around one volt, the molecule changes its structure: It becomes flat, conductive and scatters light.
This optical behavior, which differs depending on the structure of the molecule, is quite exciting for the researchers because the scattering activity - Raman scattering, in this case - can be both observed and, at the same time, switched on and off via an applied voltage.
Challenging technology
The researchers used molecules synthesized by teams based in Basel and Karlsruhe. The molecules can change their structure in specific ways when they are charged. They are arranged on a metal surface and contacted using the corner of a glass fragment with a very thin metal coating as a tip..
This serves as an electrical contact, light source and light collector, all in one. The researchers used the fragment to direct laser light to the molecule and measure tiny spectroscopic signals that vary with the applied voltage.
Contacting individual molecules electrically is extremely challenging from a technical point of view. The scientists have now successfully combined this procedure with single-molecule spectroscopy, allowing them to observe even the smallest structural changes in molecules with great precision.
Competition for Silicon
One goal of molecular electronics is to develop novel devices that can replace traditional silicon-based components using integrated and directly controllable molecules.
Thanks to its tiny dimensions, this nanosystem is suitable for applications in optoelectronics, in which light needs to be switched using variations in electrical potential.
###
The research project was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) for the Cluster of Excellence Munich-Centre for Advanced Photonics (MAP) and SPP 1243, as well as the Eropean Union (ERC Advanced Grant MolArt and FET Measure 2D-ink).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andreas Battenberg
49-892-891-0510
Copyright © Technical University of Munich (TUM)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Organic Electronics
![]() Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures August 16th, 2024
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
Hardware
![]() The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
![]() A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
![]() Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








