Home > Press > Design approach developed for important new catalysts for energy conversion and storage: New method could aid in design of pharmaceuticals and optical and data storage materials
 |
Abstract:
Northwestern University researchers have discovered a new approach for creating important new catalysts to aid in clean energy conversion and storage. The design method also has the potential to impact the discovery of new optical and data storage materials, catalysts that impact pharmaceutical synthesis and catalysts that allow for higher efficiency processing of petroleum products at much lower cost.
Design approach developed for important new catalysts for energy conversion and storage: New method could aid in design of pharmaceuticals and optical and data storage materials
Evanston, IL | Posted on March 21st, 2018Scientists are continually seeking new materials to catalyze (accelerate) the chemical reactions and processes required to create a broad range of products. Identifying and creating a catalyst is complex, especially as the potential number of materials, defined by composition and particle size and shape, is overwhelming.
In this study, researchers looked at the challenges of improving affordability and catalyst efficiency in the conversion and storage of clean energy. Currently, platinum-based (Pt) catalysts are the most effective and commonly used to facilitate a hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), which is, in part, the basis for how fuel cells are used to generate energy. However, as platinum is rare and costly, scientists have been seeking more affordable and efficient alternatives.
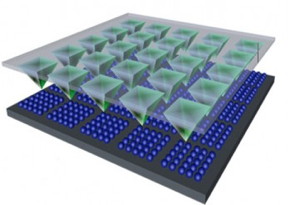
“We combined theory, a powerful new tool for synthesizing nanoparticles and more than one metallic element — in this case, an alloy consisting of platinum, copper and gold — to create a catalyst that is seven times more active than state-of-the-art commercial platinum,” said Chad A. Mirkin, the George B. Rathmann Professor of Chemistry in the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences and the director of the International Institute for Nanotechnology at Northwestern.
The study, published online this week by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), was co-authored by Mirkin; Chris Wolverton, the Jerome B. Cohen Professor of Materials Science and Engineering in Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering; and Yijin Kang, an electrochemist and visiting professor from the University of Electronic Science and Technology in China.
Specifically, researchers utilized scanning probe block copolymer lithography (SPBCL), along with density-functional theory (DFT) codes, to design and synthesize the HER catalyst. Invented in Mirkin’s lab at Northwestern, SPBCL enables scientists to control the growth and composition of individual nanoparticles patterned on a surface. The DFT codes outline the structural, magnetic and electronic properties of molecules, materials and defects.
“In addition to providing a new way to catalyze the HER reaction, the paper highlights a novel approach for making and discovering new particle catalysts for almost any industrially important process,” Wolverton said.
This may include providing a clear path to new high-temperature superconductors; structures useful in data storage; materials for solar energy conversion nanostructures to move light around at the tiniest of scales; and new catalysts for converting low-value (affordable) chemicals into high-value products, such as pharmaceuticals and pharmaceutical precursors.
Identifying new materials is essential for driving technological development. The global catalysis market is expected to reach $34.3 billion in the next six years, according to a report by Grand View Research, Inc.
“To find best-in-class materials that drive any application of interest, we need to identify ways to reduce the number of possibilities that will be studied and increase the rate at which they can be explored,” Kang said.
“This combination of theory and nanoscale particle synthesis begins to take on that challenge,” said Mirkin, who also is a professor at McCormick.
The study is titled “Catalyst design by scanning probe block copolymer lithography.”
Lilang Huang and Peng-Cheng Chen are first authors of the study.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Megan Fellman
847-491-3115
Source contact:
Chad Mirkin
847-491-2907
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








