Home > Press > Ultrathin black phosphorus for solar-driven hydrogen economy: Osaka University researchers use sunlight to make hydrogen with a new nanostructured catalyst based on nanosheets of black phosphorus and bismuth vanadate
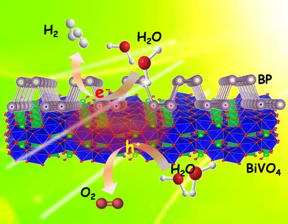 |
| Photocatalytic overall pure-water splitting using the 2-D heterostructures of BP/BiVO4 without any sacrificial agents under visible light irradiation. CREDIT Osaka University |
Abstract:
Hydrogen as a fuel source, rather than hydrocarbons like oil and coal, offers many benefits. Burning hydrogen produces harmless water with the potential to eliminate carbon dioxide emissions and their environmental burden. In pursuit of technologies that could lead to a breakthrough in achieving a hydrogen economy, a key issue is making hydrogen cheaply. Using catalysts to split water is the ideal way to generate hydrogen, but doing so usually requires an energy input from other chemicals, electricity, or a portion of sunlight which has high enough energy.
Ultrathin black phosphorus for solar-driven hydrogen economy: Osaka University researchers use sunlight to make hydrogen with a new nanostructured catalyst based on nanosheets of black phosphorus and bismuth vanadate
Osaka, Japan | Posted on January 17th, 2018Now researchers at Osaka University have developed a new catalytic system for efficiently splitting water and making hydrogen with energy from normal sunlight. Their study was recently reported in Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
"It has not been possible to use visible light for photocatalysis, but our approach of combining nanostructured black phosphorus for water reduction to hydrogen and bismuth vanadate for water oxidation to oxygen lets us make use of a wide range of the solar spectrum to make hydrogen and oxygen with unprecedented efficiency," lead author Mingshan Zhu says.
Black phosphorus has a flat, two-dimensional structure similar to that of graphene and strongly absorbs light across the whole of the visible spectrum. The researchers combined the black phosphorus with bismuth vanadate, which is a well-known water oxidation catalyst.
In the same way that plants shuttle electrons between different structures in natural photosynthesis to split water and make oxygen, the two components of this new catalyst could rapidly transfer electrons excited by sunlight. The amounts of the two components was also optimized in the catalyst, leading to production of hydrogen and oxygen gases in an ideal 2:1 ratio.
Coauthor Tetsuro Majima says, "The realization of hydrogen production powered by sunlight is the foundation of a hydrogen-oriented society. Our contribution overcomes a significant hurdle, but much work remains to be done to make hydrogen a practical fuel source in the future."
####
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and now has expanded to one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities. The University has now embarked on open research revolution from a position as Japan's most innovative university and among the most innovative institutions in the world according to Reuters 2015 Top 100 Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017. The university's ability to innovate from the stage of fundamental research through the creation of useful technology with economic impact stems from its broad disciplinary spectrum.
Website: http://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en/top
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Saori Obayashi
81-661-055-886
Copyright © Osaka University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








