Home > Press > Drug-delivering nanoparticles seek and destroy elusive cancer stem cells
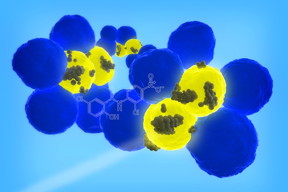 |
| Illinois researchers developed nanoparticles that can target cancer stem cells (yellow), the rare cells within a tumor (blue) that can cause cancer to recur or spread. Image courtesy of Dipanjan Pan |
Abstract:
University of Illinois researchers are sending tiny drug-laden nanoparticles on a mission to seek and destroy cancer stem cells, the elusive and rare cells that can cause cancer to come back even when years have passed since the initial tumor was treated.
Drug-delivering nanoparticles seek and destroy elusive cancer stem cells
Champaign, IL | Posted on November 28th, 2017In a study led by Dipanjan Pan, an Illinois professor of bioengineering, researchers designed nanoparticles that specifically bind to a protein that marks the surface of breast cancer stem cells. Encapsulated in the particles is the drug niclosamide – a drug commonly prescribed around the world to treat tapeworm infections, but in cancer stem cells it turns off key gene pathways that give the cells the stemlike properties that enable them to grow and spread.
“It is critical to administer treatments for already-developed tumors; however, long-term survival and not allowing it to come back are equally important,” Pan said. “We want to destroy the cells that are hidden in the tissue and cause the cancer to come back or spread to other parts of the body.”
Cancer stem cells represent a tiny fraction of cells in a tumor, but it only takes one or two to seed a new tumor, Pan said. The challenge for physicians and researchers is not only finding these cells, but treating them. Pan’s group created nanoparticles that target a protein called CD44, which only appears on the surface of cancer stem cells, and tested them on breast cancer tumors in cell cultures and in live mice.
“I call them ‘GPS-enabled nanoparticles,’ because they seek out only the cells that have cancer stem cell properties. Then they latch onto the cells and deliver the drug,” said Pan, also a faculty member of the Carle Illinois College of Medicine and the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology. “To the best of our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of delivering cancer stem-cell-targeted therapy with a nanoparticle.”
The researchers used the nanoparticles to deliver niclosamide, which is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines, an index of the safest and most effective drugs in the world. Pan’s group previously found that niclosamide works on a particular gene-regulation pathway in cancer stem cells.
In the new study published in the journal Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, the cancer stem cells lost their stemlike properties after treatment with the niclosamide-bearing targeted nanoparticles, making them less able to cause the cancer to recur or metastasize. The researchers also saw a significant decrease in overall cancer cell growth, both in the cell cultures and in the mice.
By using an already-approved drug and easy-to-manufacture nanoparticles, Pan hopes that this system can become an accessible and cost-efficient treatment to prevent cancer recurrence in patients
“We purposely used an extremely inexpensive drug. It’s generic and we can mass produce it on a very large scale,” Pan said. “The nanoparticles are a polymer that we can make on a large scale – it’s highly defined and consistent, so we know exactly what we are delivering. The rest of the process is just self-assembly.”
“This work also is important to future researchers working in the field of cancer stem cells,” said postdoctoral researcher Santosh Misra, the first author of the study. “We described and confirmed the proteins and genes responsible for vital processes in these cells, and that is opening up new avenues to make better therapies.”
The researchers are working to create a combination therapy that can deliver drugs for the primary cancer, such as traditional chemotherapies, as well as targeted agents that can treat cancer stem cells. They are also testing the nanoparticle drug-delivery system in large animal models to bring it a step closer to the clinic.
The National Institutes of Health and the University of Illinois supported this work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
LIZ AHLBERG TOUCHSTONE
BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES EDITOR
217-244-1073
Dipanjan Pan
217-244-2938
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








