Home > Press > ICN2 researchers compute unprecedented values for spin lifetime anisotropy in graphene
 |
Abstract:
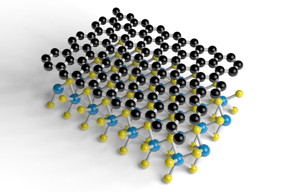
Researchers of the ICN2 Theoretical and Computational Nanoscience Group, led by ICREA Prof. Stephan Roche, have published another paper on spin, this time reporting numerical simulations for spin relaxation in graphene/TMDC heterostructures. Published in Physical Review Letters, their calculations indicate a spin lifetime anisotropy that is orders of magnitude larger than anything observed in graphene until now. Here, lead author Aron Cummings explains the origin of this effect.
ICN2 researchers compute unprecedented values for spin lifetime anisotropy in graphene
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on November 17th, 2017Published in Physical Review Letters this week, spintronics researchers of the ICN2 Theoretical and Computational Nanoscience Group led by ICREA Prof. Stephan Roche have gleaned potentially game-changing insight into the mechanisms governing spin dynamics and relaxation in graphene/TMDC heterostructures. Not only do their models give a spin lifetime anisotropy that is orders of magnitude larger than the 1:1 ratio typically observed in 2D systems, but they point to a qualitatively new regime of spin relaxation.
Spin relaxation is the process whereby the spins in a spin current lose their orientation, reverting to a natural disordered state. This causes spin signal to be lost, since spins are only useful for transporting information when they are oriented in a certain direction. This study reveals that the rate at which spins relax in graphene/TMDC systems depends strongly on whether they are pointing in or out of the graphene plane, with out-of-plane spins lasting tens or hundreds of times longer than in-plane spins. Such a high ratio has not previously been observed in graphene or any other 2D material.
In the paper, aptly titled “Giant Spin Lifetime Anisotropy in Graphene Induced by Proximity Effects”, lead author Aron Cummings reports that this behaviour is mediated by the spin-valley locking induced in graphene by the TMDC, which ties the lifetime of in-plane spin to the intervalley scattering time. This causes in-plane spin to relax much faster than out-of-plane spin. Furthermore, the numerical simulations suggest that this mechanism should come into play in any substrate with strong spin-valley locking, including the TMDCs themselves.
Effectively inducing a spin filter effect –the ability to sort or tweak spin orientations–, these findings give reason to believe that it might one day be possible to manipulate, and not just transport, spin in graphene.
These simulations have since been borne out experimentally by colleagues in the ICN2 Physics and Engineering of Nanodevices Group, led by ICREA Prof. Sergio Valenzuela. Paper coming soon.
####
About ICN2
The Institut Català de Nanociència i Nanotecnologia, with its official English translation Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology and acronym ICN2, is a non-profit international research institute located close to Barcelona, Spain. Its research lines focus on the newly-discovered physical and chemical properties that arise from the behaviour of matter at the nanoscale.
The patrons of the ICN2 are the Government of Catalonia, the Spanish National Research Council and the Autonomous University of Barcelona. The institute promotes collaboration among scientists from diverse backgrounds to develop basic and applied research, while always seeking out new ways to engage with local and global industry. The ICN2 also trains researchers in nanotechnology, develops numerous activities to facilitate the uptake of nanotechnology by industry, and promotes networking among scientists, engineers, technicians, business people, society, and policy makers.
The ICN2 was accredited by the Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness as a Severo Ochoa Centre of Excellence in 2014, the highest level of recognition of scientific excellence and leadership that can be bestowed on a research centre in Spain.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Rachel Spencer
Phone: +34 93 737 26 71
Copyright © ICN2
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








