Home > Press > Scientists discover new magnet with nearly massless charge carriers
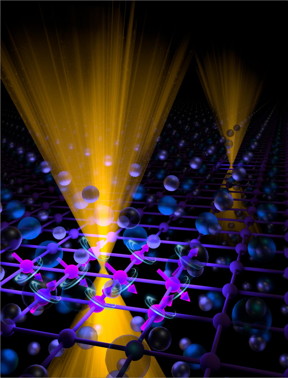 |
| The magnetic and electronic states of newly discovered Sr1-yMn1-zSb2 are depicted by spheres representing the positions of the atoms in the crystal structure of this material with strontium (Sr) depicted by the small violet spheres; antimony (Sb) by the large blue spheres; and manganese (Mn) by the purple spheres. The arrows attached to the Mn atoms represent the magnetic moments of these atoms which align in the orientation shown to give the magnetic properties of Sr1-yMn1-zSb2. Also depicted are the energy and momentum states of the conducting electrons, or charge carriers, which have a Dirac-like dispersion relation shown in gold. CREDIT Oak Ridge National Laboratory |
Abstract:
Advances in modern electronics has demanded the requisite hardware, transistors, to be smaller in each new iteration. Recent progress in nanotechnology has reduced the size of silicon transistors down to the order of 10 nanometers. However, for such small transistors, other physical effects set in, which limit their functionality. For example, the power consumption and heat production in these devices is creating significant problems for device design. Therefore, novel quantum materials and device concepts are required to develop a new generation of energy-saving information technology. The recent discoveries of topological materials -- a new class of relativistic quantum materials -- hold great promise for use in energy saving electronics.
Scientists discover new magnet with nearly massless charge carriers
Baton Rouge, LA | Posted on July 29th, 2017Researchers in the Louisiana Consortium for Neutron Scattering, or LaCNS, led by LSU Department of Physics & Astronomy Chair and Professor John F. DiTusa and Tulane University Professor Zhiqiang Mao, with collaborators at Oak Ridge National Lab, the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Florida State University, and the University of New Orleans, recently reported the first observation of this topological behavior in a magnet, Sr1-yMn1-zSb2 (y, z < 0.1). These results were published this week in Nature Materials (doi:10.1038/nmat4953).
"This first observation is a significant milestone in the advancement of novel quantum materials and this discovery opens the opportunity to explore its consequences. The nearly massless behavior of the charge carriers offers possibilities for novel device concepts taking advantage of the extremely low power dissipation," DiTusa said.
The phrase "topological materials" refers to materials where the current carrying electrons act as if they have no mass similar to the properties of photons, the particles that make up light. Amazingly, these electronic states are robust and immune to defects and disorder because they are protected from scattering by symmetry. This symmetry protection results in exceedingly high charge carrier mobility, creating little to no resistance to current flow. The result is expected to be a substantial reduction in heat production and energy saving efficiencies in electronic devices.
This new magnet displays electronic charge carriers that have almost no mass. The magnetism brings with it an important symmetry breaking property - time reversal symmetry, or TRS, breaking where the ability to run time backward would no longer return the system back to its starting conditions. The combination of relativistic electron behavior, which is the cause of much reduced charge carrier mass, and TRS breaking has been predicted to cause even more unusual behavior, the much sought after magnetic Weyl semimetal phase. The material discovered by this collaboration is thought to be an excellent one to investigate for evidence of the Weyl phase and to uncover its consequences.
###
The researchers involved include J.Y. Liu, J. Hu, Y.L. Zhu, G.F. Cheng, X. Liu, J. Wei, and Z.Q. Mao (Tulane University, New Orleans); Q. Zhang, W. A. Phelan, and J. F. DiTusa (Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge); D. Graf, (National High Magnetic Field Lab, Tallahassee); Q. Zhang, H.B. Cao and D. A. Tennant (Oak Ridge National Laboratory); S.M.A. Radmanesh, D.J. Adams, and L. Spinu (University of New Orleans); Marcelo Jaime and Fedor Balakirev (Condensed Matter and Magnet Science, MPA-CMMS); and I. Chiorescu (NHFML and Florida State University, Tallahassee).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Alison Satake
225-578-3870
Copyright © Louisiana State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








